Introduction
In order to model fluid-structure interaction with OS one should consider the type of fluid he wants to study. One way is to look at the bulk modulus of the material that can be defined as:
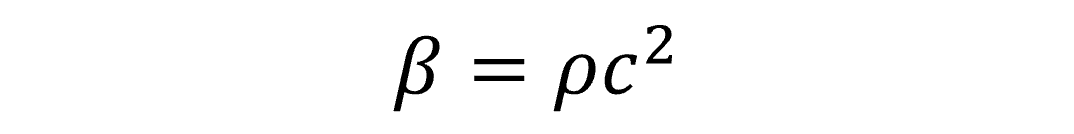
where ρ is the density and c is the speed of sound. Since compressibility is the inverse of the bulk modulus, fluids with high β are considered incompressible or nearly incompressible, instead fluids with low β are considered compressible. For example, bulk modulus of water is around 2011MPa, of air is 0.118 MPa.
FSI can be modeled in two ways in OS:
- with virtual fluid mass approach, that is a method to mimic the behavior of fluids inside recipients without the need to create an explicit mesh for the fluid;
- with acoustic coupling and explicit fluid modeling with mesh, material and property.

Figure 1: VFM |

Figure 2: Acoustic FSI |
|---|
|
The attached .pdf discusses the best method to model compressible and incompressible fluids with OptiStruct. Comparison with experimental test is also provided.
For additional in-depth analysis of virtual fluid mass method you can refer to this article: Virtual Fluid Mass
For acoustic coupling method you can refer to: Coupled Frequency Response Analysis of Fluid-Structure Models