Highlights of the 2024.0 Release
Feko
The Feko 2024.0 release features extensions to many different solvers - enhancing Feko's capabilities in propagation modelling, network planning as well as general and specialist EM analysis application areas. There are various performance improvements, interoperability and API extension, enabling more flexible workflows and automation.
Cables
Realistic connections from termination points of cable signals modelled using the combined MoM/MTL to arbitrary 3D geometry modelled using the MoM are now supported. This makes it possible to accurately model both radiation and conduction at cable connectors, including effects such as imperfect shielding, pigtails and actual core conductor routing.

Modelling of a realistic connection between a double-shielded dual-core cable and a circuit board using combined MoM/MTL.
Support for Lossy Dielectrics in the CBFM and MLFMM+CBFM

Computation of RCS using CBFM for a cone-sphere coated with a lossy dielectric material. Using this approach large reductions in memory and runtime requirements can be achieved (approximately 13 times less time and memory needed for the example below when compared to MoM).
Component Library
The following components were added to the component library:
- Almond
- Ogive
- Double-Ogive
- Cone-Sphere (with gap)
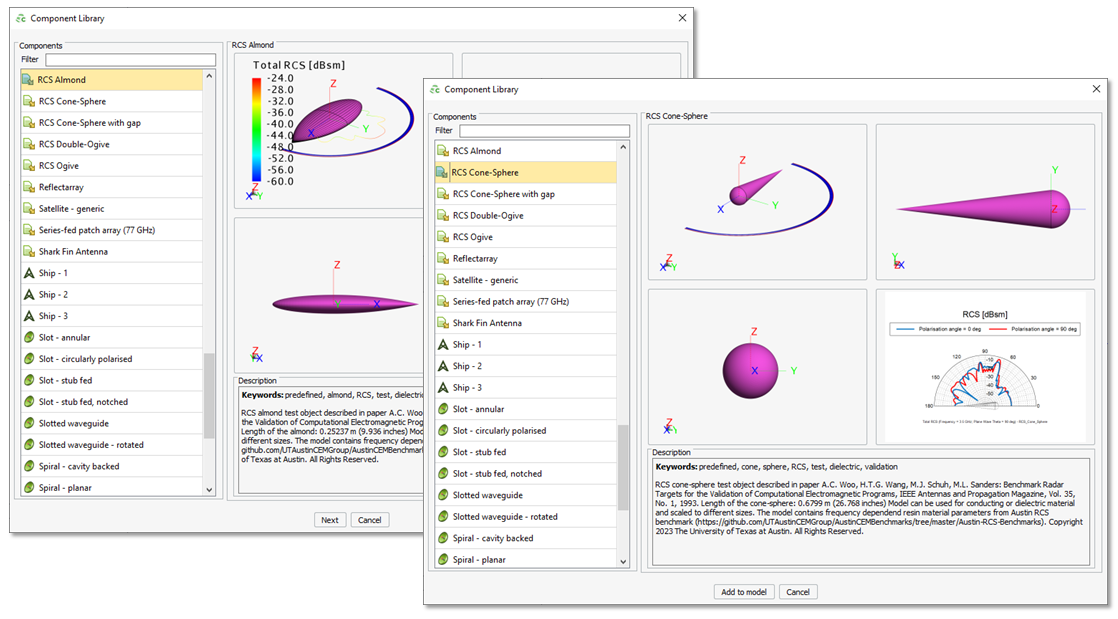
The RCS Almond and RCS Cone-Sphere components available in the Feko 2024 component library.
WinProp
MPI
The Standard Ray Tracing (SRT) method in ProMan was extended to support parallelisation using the Message Passing Interface (MPI).
Reporting
ProMan now supports the automatic generation of a Microsoft Word report that contains the project name, date and an exported image of each result with a title indicating the result type.
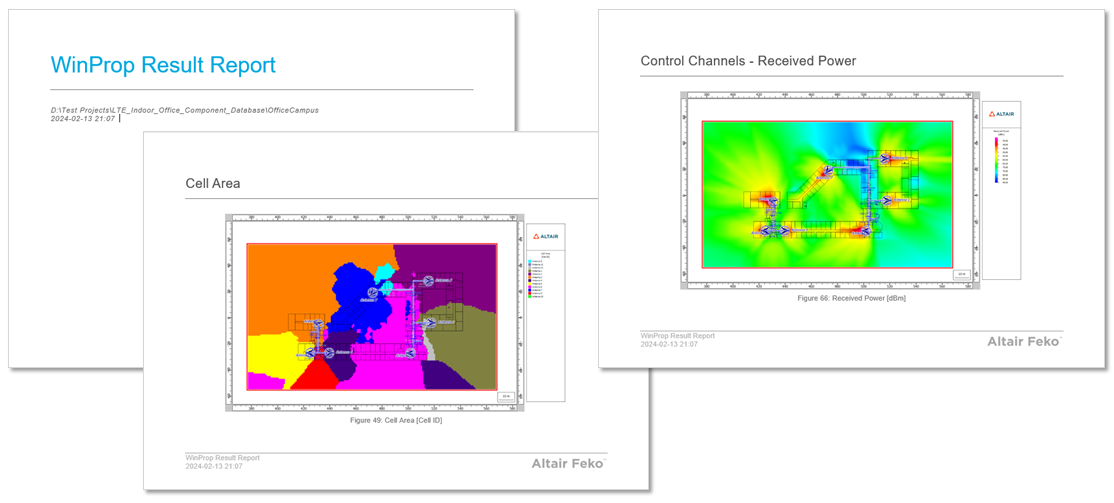
An exported Microsoft Word report showing the exported result images
2D Display
The 2D view was extended to overlay results with transparency on the topography bitmap.
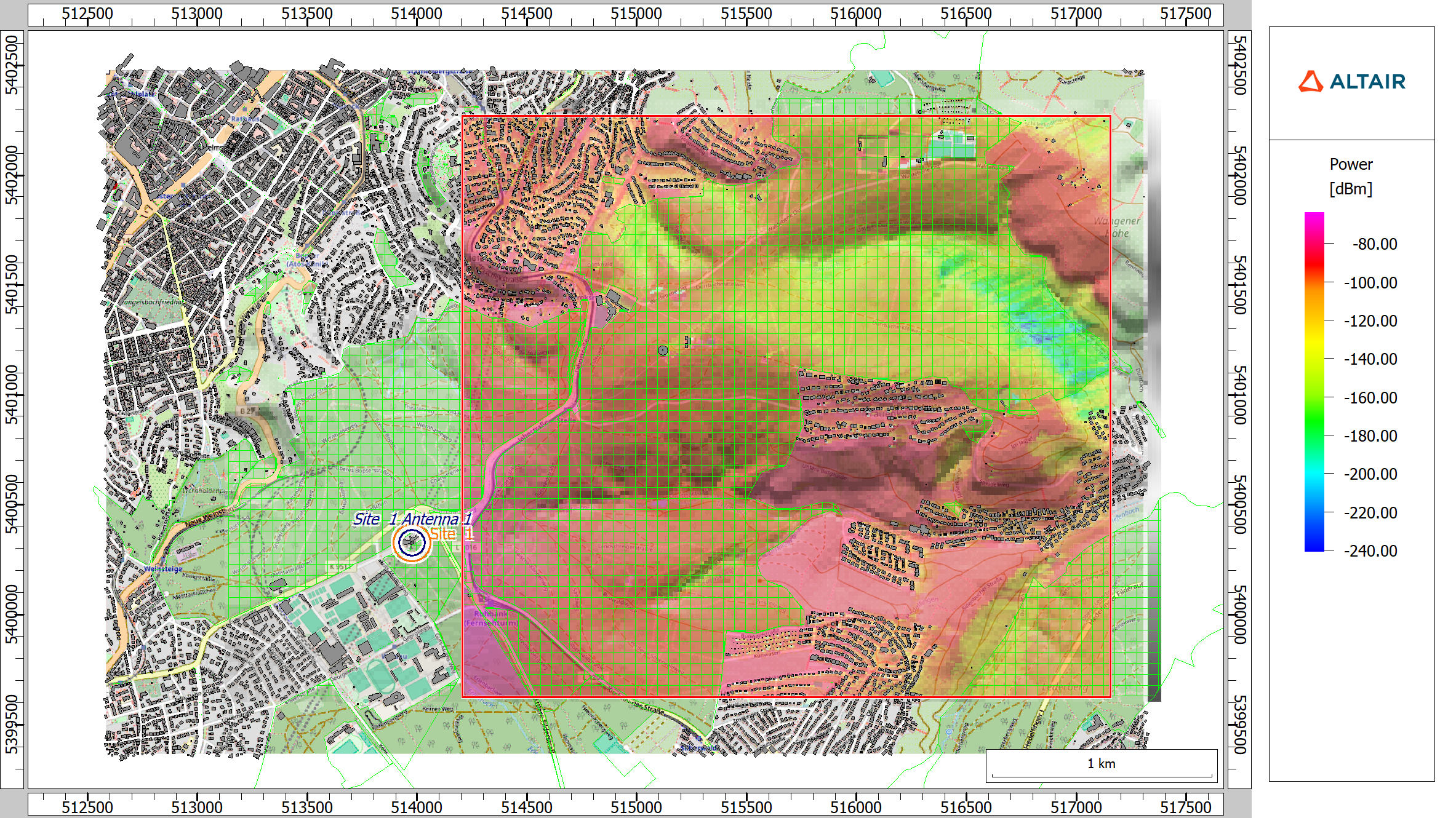
An example of transparent results over the topography bitmap.
Default Vegetation Properties
Default vegetation properties were added for 16 frequency bands from 450 MHz to 300 GHz. These properties are also relevant to furniture when an urban database is converted to a full 3D scenario using the “indoor” format.
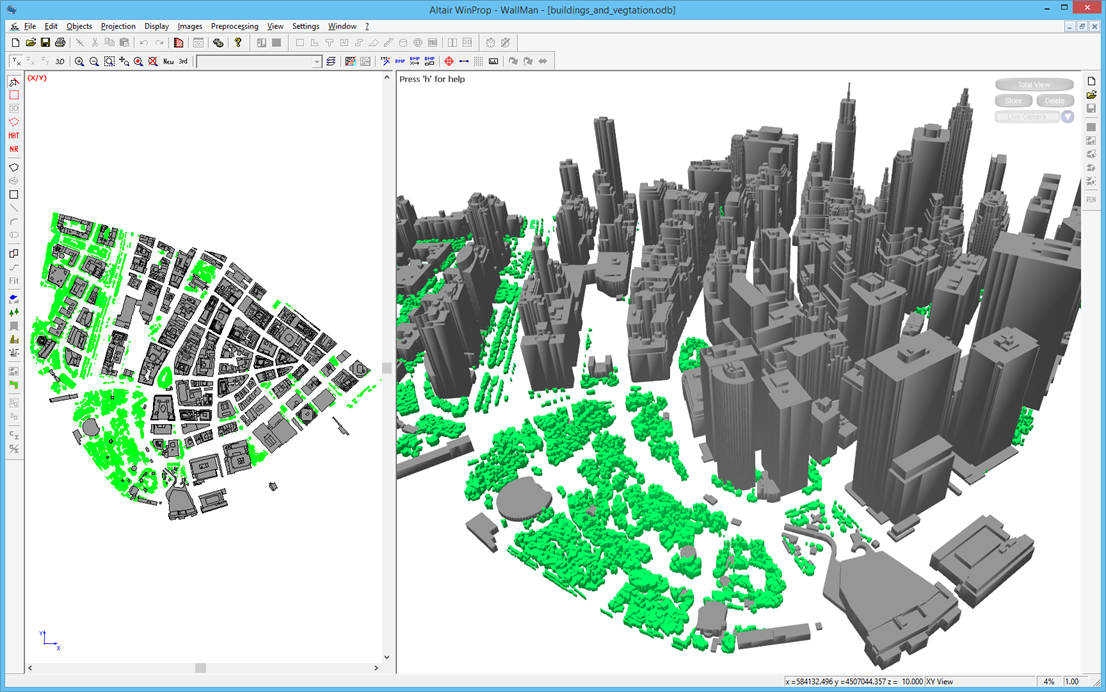
An example of an urban database (.odb file showing the vegetation in New York (Manhattan). The vegetation losses can now be considered from 450 MHz to 300 GHz.
Bistatic RCS
Bistatic RCS (computed in Feko for a single incidence direction) can now be considered when computing the wave propagation in WinProp in addition to using monostatic RCS. For the incidence direction, a tolerance of 10° is applied. This feature is useful when, for example, a detailed geometry like a windmill is to be considered for a larger propagation scenario or for the consideration of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) towards 6G.
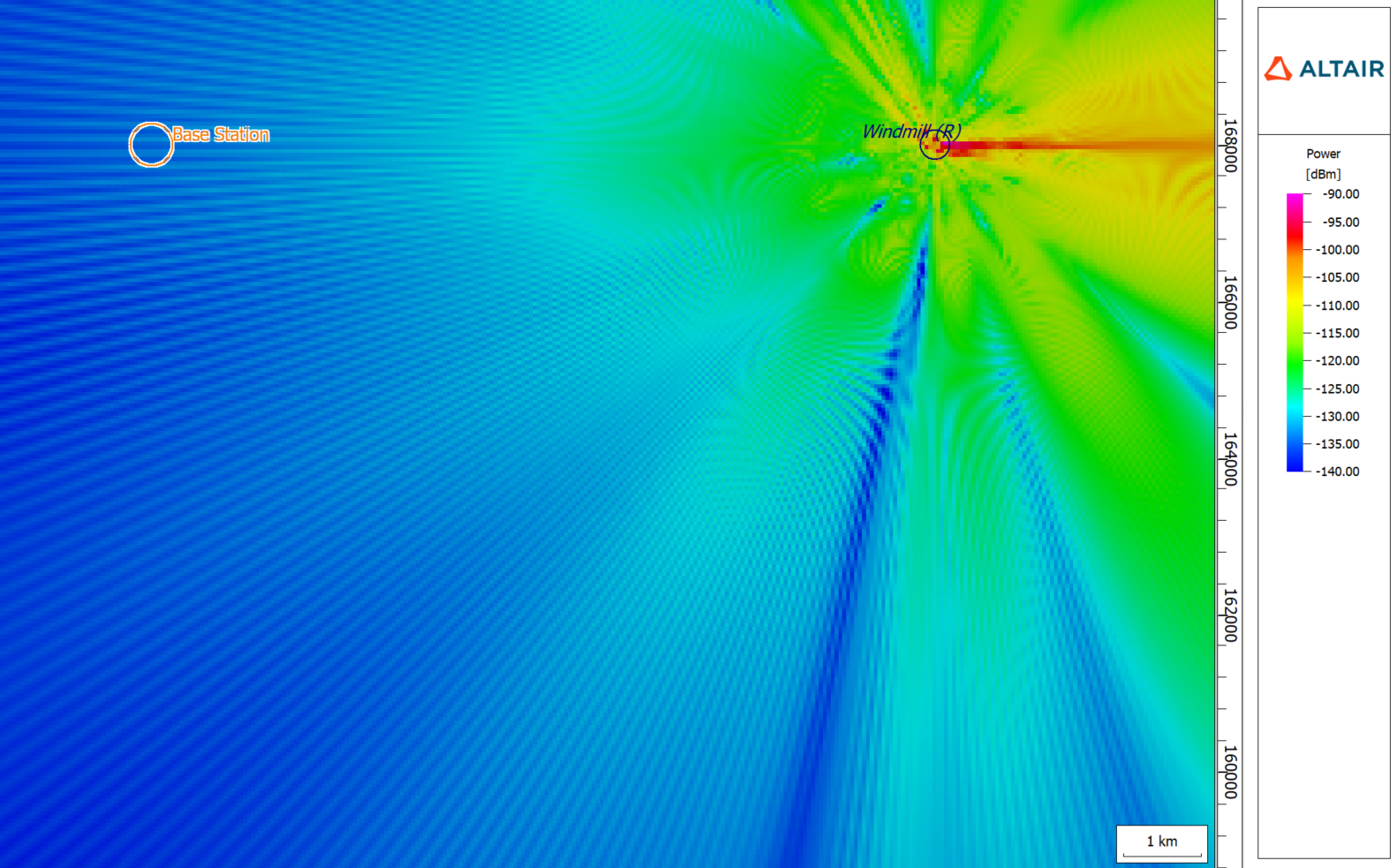
An example of where a windmill is considered in a larger propagation scenario.
WRAP
Support for Large GeoTIFF Files
GeoTIFF image files larger than 2 GB can now be converted, including GeoTIFF files using PACKBITS compression.
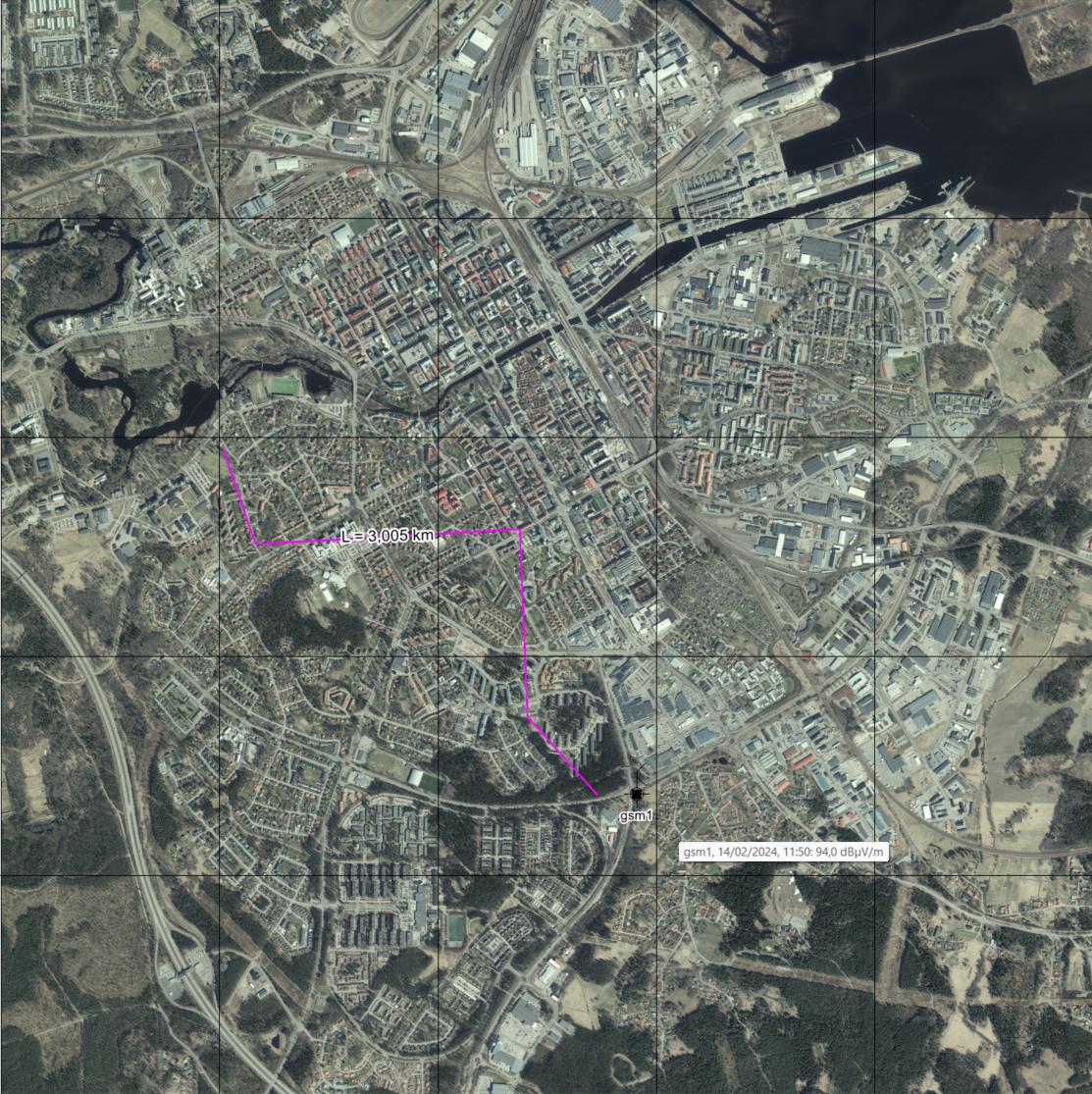
An example of a GeoTIFF image file with a size larger than 2 GB that was converted.
Equipment Type Circulator
The equipment type Circulator is now available WRAP. A circulator is set on the transmitter side of a station to reduce incoming signals that might generate Tx intermodulation that could be interfering with receivers.
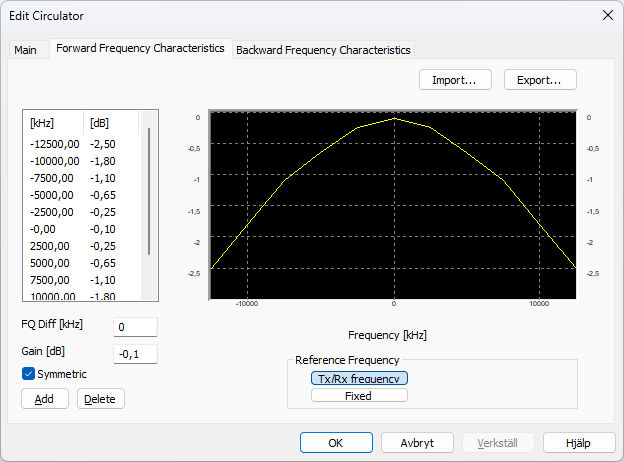
The Edit Circulator dialog where the new equipment type can be edited.
ITU-R P.530-18 Propagation Model
The ITU-R P.530-17 propagation model was updated to ITU-R P.530-18.
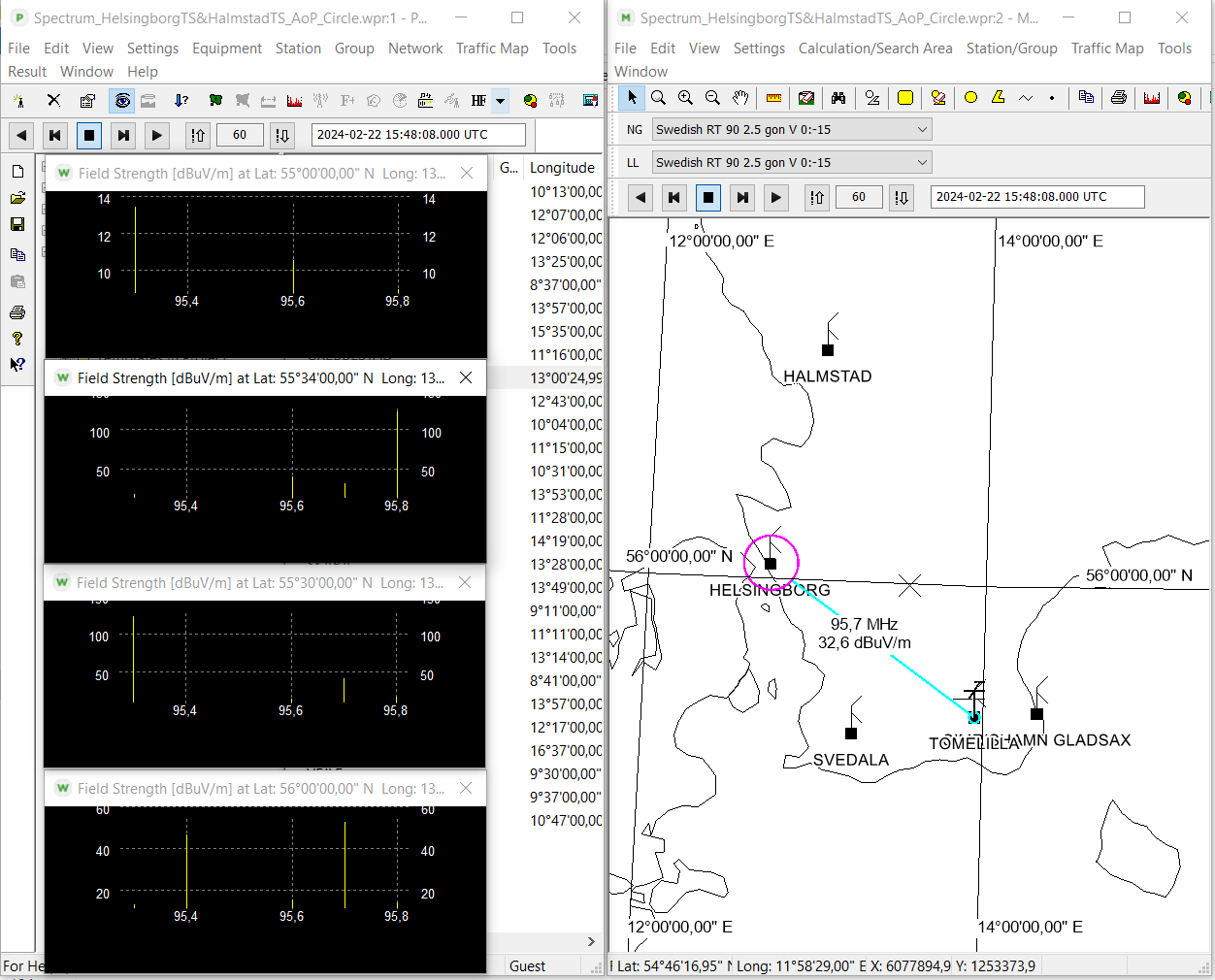
Spectrum Viewer Tool
The function in the Spectrum Viewer tool was extended to include typical stations in the calculation.
A database can now be imported in WRAP ChangeDB by right-clicking on a selected database. The import feature replaces the existing selected database with the new one and deletes the existing log file. The existing database file is backed up, and the original database is restored in case of failure.
WRAP Databases
A database can now be imported in WRAP ChangeDB by right-clicking on a selected database. The import feature replaces the existing selected database with the new one and deletes the existing log file. The existing database file is backed up, and the original database is restored in case of failure.