Author: Randy Betancourt
Date: August 2025
ContextAltair Workbench on Windows provides a development environment for SAS language programs with remote execution capabilities. This architecture allows users to edit and modify programs locally on Windows while executing them on remote Linux servers running SLC instances.
Authentication Challenge:
The built-in SSH key generation in SLC Workbench limits RSA keys with 1024-bit length. However, modern Linux distributions have implemented stricter security policies that consider 1024-bit keys insufficient and reject the ssh-rsa signature algorithm by default.
Deployment Scenarios:
- Development Environment: Windows workstation running SLC Workbench
- Execution Environment: Remote RHEL server running SLC
- Authentication Method: SSH public key authentication
- Network Communication: Encrypted SSH connections for program transfer and execution
Security Evolution Impact:
RHEL 9.6 and later versions implement system-wide crypto policies prioritizing modern cryptographic standards. These policies automatically reject older algorithms including:
- RSA keys are shorter than 2048 bits
- ssh-rsa signature algorithm (deprecated in favor of rsa-sha2-256/512)
- Legacy cipher suites and MAC algorithms
OverviewThis guide configures SSH key authentication for Altair Workbench remote execution on RHEL systems. Altair Workbench requires specific RSA key formats and RHEL systems need configuration change to accept legacy SSH signature algorithms.
Why these changes are needed:
- Constraint: Altair Workbench generates RSA key lengths of 1024 bits. Instead, RSA keys with 2048-bit lengths are generated outside of Workbench for this scenario
- Security Policy Evolution: RHEL has implemented stricter crypto policies that reject ssh-rsa signatures by default
- Operational Requirement: Organizations need Altair Workbench functionality while maintaining reasonable security posture
- Risk Mitigation: Targeted policy adjustment minimizes security exposure while enabling required functionality
Solution Approach:
Rather than compromising security broadly, this guide implements a targeted crypto policy modification to enable ssh-rsa signatures while maintaining modern security controls. This approach balances application support with contemporary security requirements.
Key Requirements Summary
- Key Type: RSA 2048-bit (enhanced from Altair Workbench's 1024-bit default)
- Format: PEM format for Windows Altair Workbench, OpenSSH public key format for Linux
- RHEL Configuration: Selective crypto policy modification to accept ssh-rsa key signatures
- Security Posture: Minimal necessary changes to maintain broad security compliance
Generate SSH Keys for SLC Workbench
Create Windows .ssh directory
mkdir C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh
cd C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh
Generate RSA 2048-bit key in PEM format
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -C "RHEL-SLC" -m pem -f slc_wb_2048_pem
Rename for clarity
ren slc_wb_2048_pem slc_wb_2048_pem.pem
Set permissions for private keys
Remove inheritance and grant only your user account full control
icacls "C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh\slc_wb_2048.ppk" /inheritance:r
icacls "C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh\slc_wb_2048.ppk" /grant:r "%USERNAME%:(F)"
Same for the PEM file
icacls "C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh\slc_wb_2048_pem.pem" /inheritance:r
icacls "C:\Users%USERNAME%.ssh\slc_wb_2048_pem.pem" /grant:r "%USERNAME%:(F)"
Verify permissions
icacls "C:\Users\%USERNAME%\.ssh\slc_wb_2048_pem.pem"
C:\Users\<username>\.ssh\slc_wb_2048_pem.pem BUILTIN\Administrators:(F)
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(F)
PROG\<username>:(F)
Key File Usage Summary
File | Format | Used By |
|---|
.ppk | PuTTY Private | PuTTY, WinSCP |
.pem | OpenSSH Private | SLC Workbench, SSH clients |
.pub | SSH Public | Linux server authorized_keys |
Configure RHEL System Crypto Policy
Critical: RHEL 9.6+ uses system crypto policies that reject ssh-rsa signatures by default. This must be modified for SLC Workbench compatibility.
Check current crypto policy
sudo update-crypto-policies --show
DEFAULT:
Set policy to allow ssh-rsa signatures
sudo update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:SHA1
DEFAULT:SHA1
Restart SSH service
sudo systemctl restart sshd
Verify ssh-rsa is now accepted
sudo sshd -T | grep -i pubkeyaccepted
pubkeyacceptedalgorithms ecdsa-sha2-nistp256, ecdsa-sha2-
nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com, sk-ecdsa-sha2-
nistp256@openssh.com, sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-
v01@openssh.com, ecdsa-sha2-nistp384, ecdsa-sha2-nistp384-cert-
v01@openssh.com, ecdsa-sha2-nistp521, ecdsa-sha2-nistp521-cert-
v01@openssh.com, ssh-ed25519,ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com, sk-
ssh-ed25519@openssh.com,sk-ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com, rsa-
sha2-256, rsa-sha2-256-cert-v01@openssh.com, rsa-sha2-512, rsa-
sha2-512-cert-v01@openssh.com, ssh-rsa,ssh-rsa-cert-v01@openssh.com
Expected output should end with: ssh-rsa,ssh-rsa-cert-v01@openssh.com
Success indicators:
- Crypto policy shows: DEFAULT:SHA1
- SSH algorithms list includes ssh-rsa at the end
- No system restart needed (SSH service restart is sufficient)
User Groups and UsersCreate sasusers group for SLC users
sudo groupadd sasusers
Add existing user to sasusers group
sudo usermod -a -G sasusers ec2-user
Create new user account
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash trb
Set password for new user
sudo passwd trb
Add new user to group sasusers
sudo usermod -a -G sasusers trb
Verify group membership
groups ec2-user
groups trb
groups trb
trb : trb sasusers
Install Public KeysFor ec2-user account
mkdir -p ~/.ssh
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
Add public key
paste content from slc_wb_2048_pem.pub from Windows
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2E... [paste-your-key-here]" >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Test SSH Connections
Test connection to ec2-user
ssh -i slc_wb_2048_pem.pem ec2-user@YOUR _SERVER_IP
Test PuTTY Connection
- Open PuTTY
- Host Name: Your server IP
- Port: 22
- Connection → SSH → Auth: Browse to slc_wb_2048.ppk
- Open connection
Configure SLC WorkbenchMake private key known to Workbench
Windows -> Preferences -> General -> Network Connections -> ssh
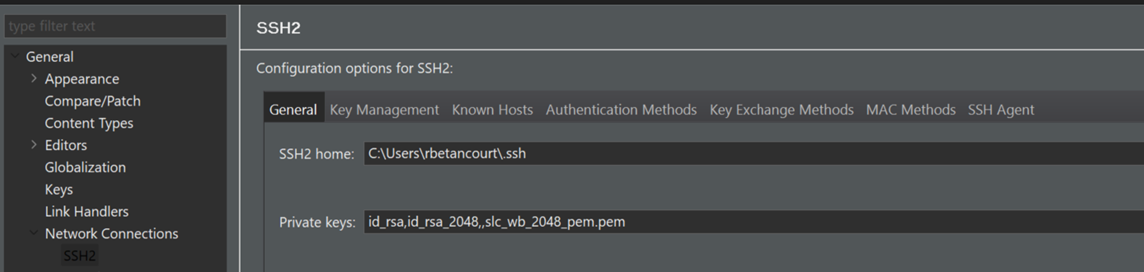
Add the Windows private key to the list of Private keys
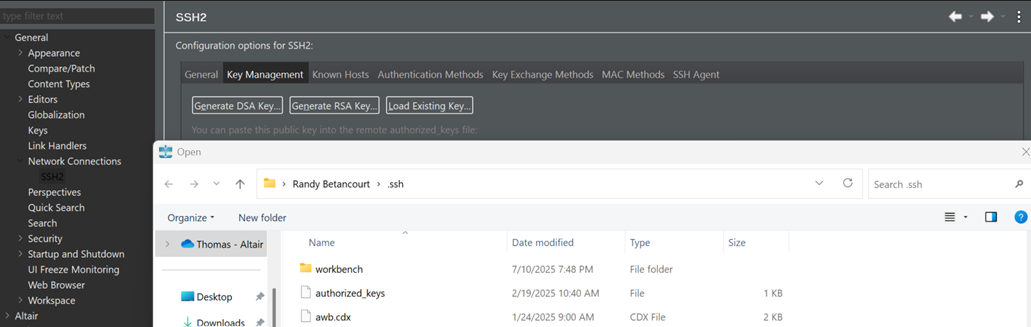
Test private key with Workbench
Select Key Management and Load Existing Key
Confirm public key
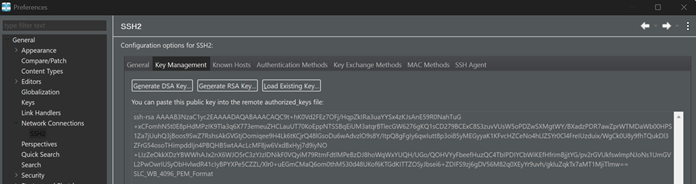
This is the same public key pasted in the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on Linux performed in a previous step. This public key values must match the private key stored on Windows.
Define New Host Connection
Link Explorer -> Right Mouse Button
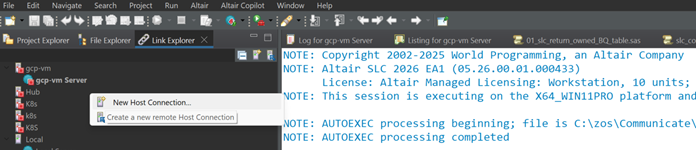
New SSH Connection
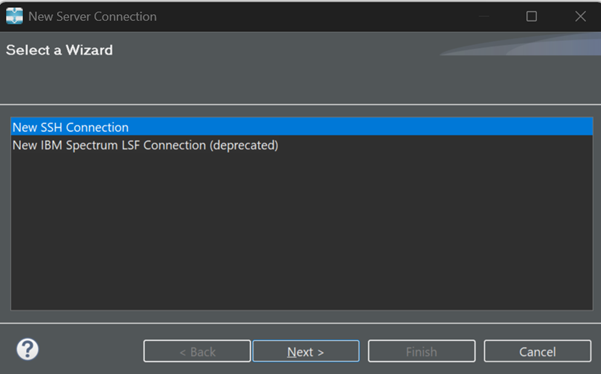
New Remote Host Connection
In SLC Workbench remote execution setup:
- Windows Private Key: C:\Users\%USERNAME%\.ssh\slc_wb_2048_pem.pem
- Host: Your remote hostname or IP address
- Port: 22
- Username: user identity
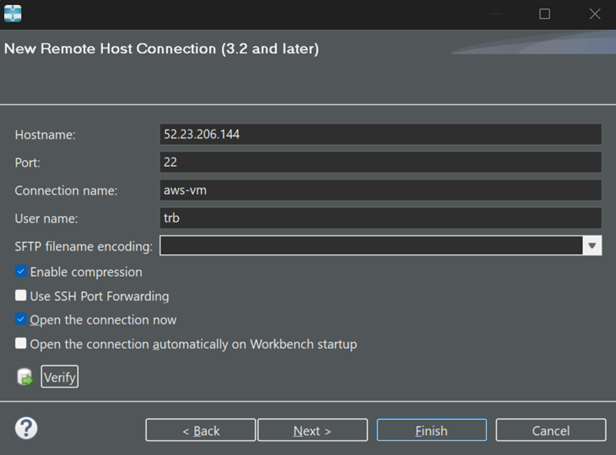
Press Finish. You receive a one-time message since the remote host IP address is not found in the local known hosts file.
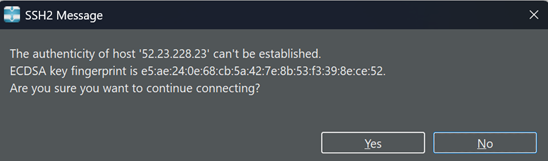
Press Yes.
Define Altair SLC Server
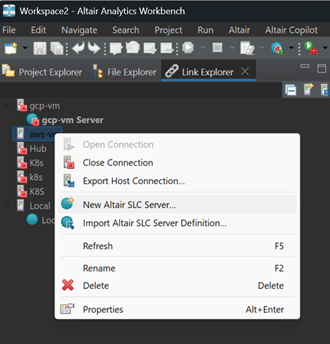
This is a one-time set-up. The server definition is saved by Altair Workbench.
Locate SLC Home Directory Path
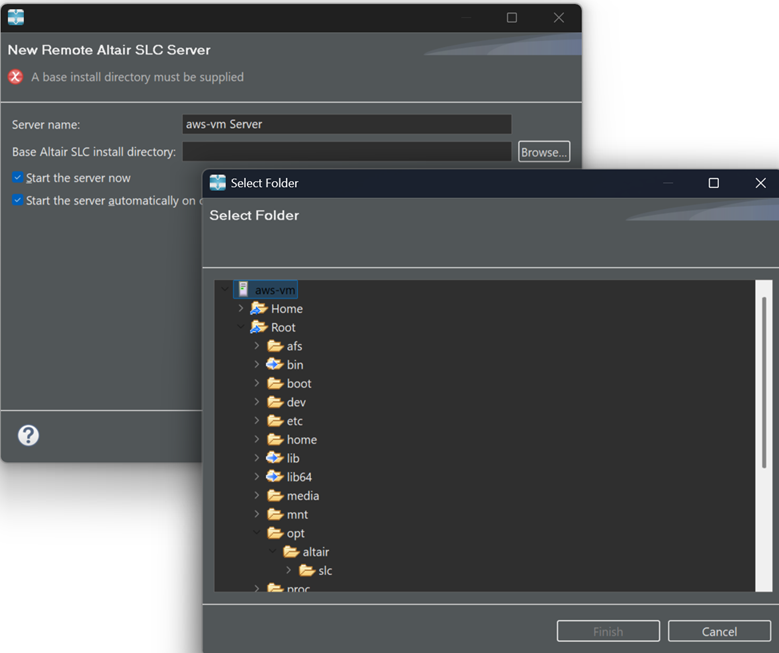
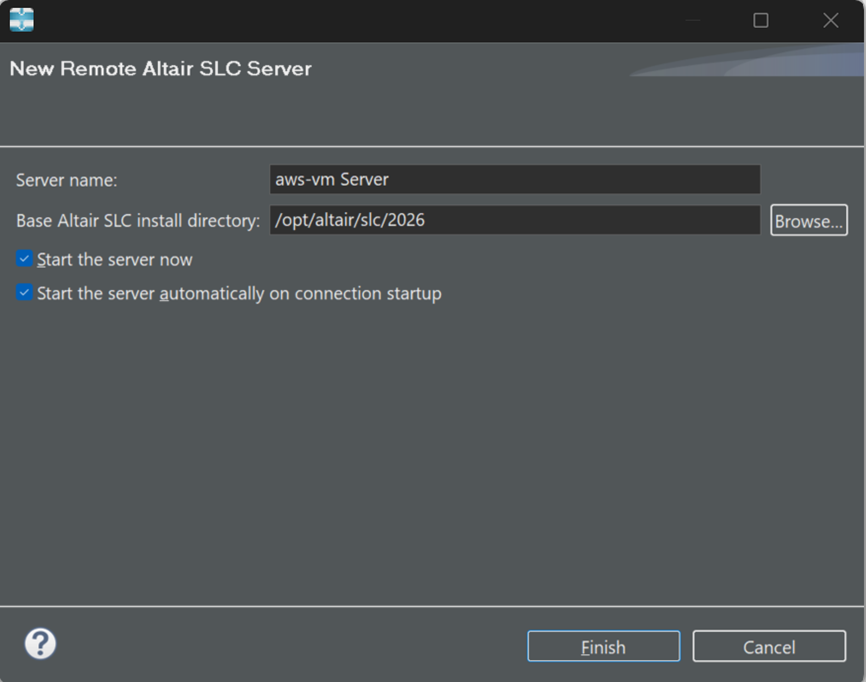
Navigate to the SLC home directory for your site. This is usually: /opt/altair/slc/2026
Start/Stop: Restart SLC Server
Link Explorer -> Select Server -> Right Mouse Button
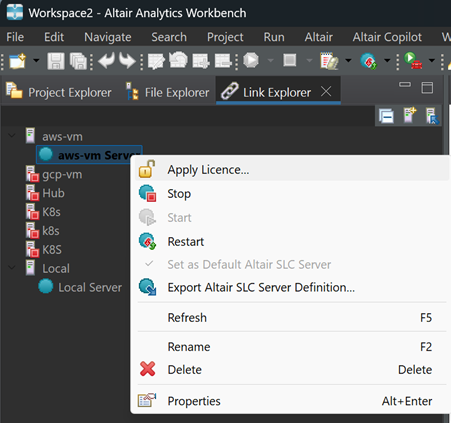
STOP ends the SLC instance running on the server, deleting temporary data in SASWORK.
RESTART recycles the SLC instance on the server by first clearing the log file, emptying the global and local macro symbol tables, deleting temporary files in SASWORK. Then initializes a new instance of SLC, runs the shell script altairsclenv.sh in the SLC home directory, and performs AUTOEXEC processing (if present).
RESTART is useful when debugging macro programs to ensure a newly initialized environment is used for test and development purposes.