This article demonstrates how to use PSIM CodeGen for configuring Trip Zones, X-BARs, and related PWM control strategies for:
- Peak current control
- Phase-synchronized PWM
Advanced power converter control often demands PWM generation beyond simple duty-cycle modulation. Two common but complex scenarios include:
1. Peak Current Mode Control (PCMC)
In PCMC, PWM must terminate precisely when the sensed current reaches a reference peak. While this is simple in simulation using comparators, implementing it on hardware requires real-time event-driven control using modules like Trip Zone and X-BAR. Traditional embedded C coding for these peripherals is non-trivial and error prone.
2. Phase-synchronized PWM
In converters like PSFB, secondary-side PWM pulses must be synchronized with the primary bridge. These interdependencies can’t be handled by standard PWM modules and require event routing logic, often through X-BAR or Trip Zones.
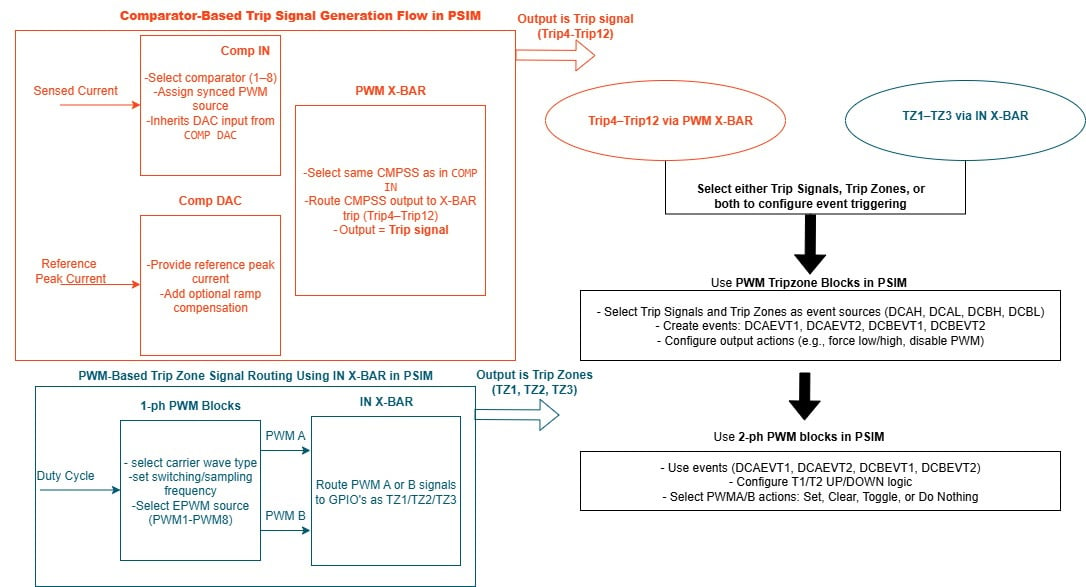
Fig 1: Overview of PWM generation with PSIM Blocks
Application Example: Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge (PSFB) Converter with Active Secondary
To demonstrate the concepts discussed above—Trip Signals, Trip Zones, and event-based PWM generation—we consider a Phase-Shifted Full-Bridge (PSFB) converter with an actively controlled secondary stage. Two specific cases are illustrated. Here in this PART-I, we discuss Open-loop Operation.
1. Open-Loop Operation
- The primary-side bridge operates with a fixed phase shift.
- The secondary-side PWM pulses are generated based on:
- The timing of the primary bridge switches, routed via IN X-BAR.
- Conditional logic using Trip Zones (TZ1–TZ3) to define gating conditions.
- PSIM CodeGen is used to automatically configure routing and event setup.
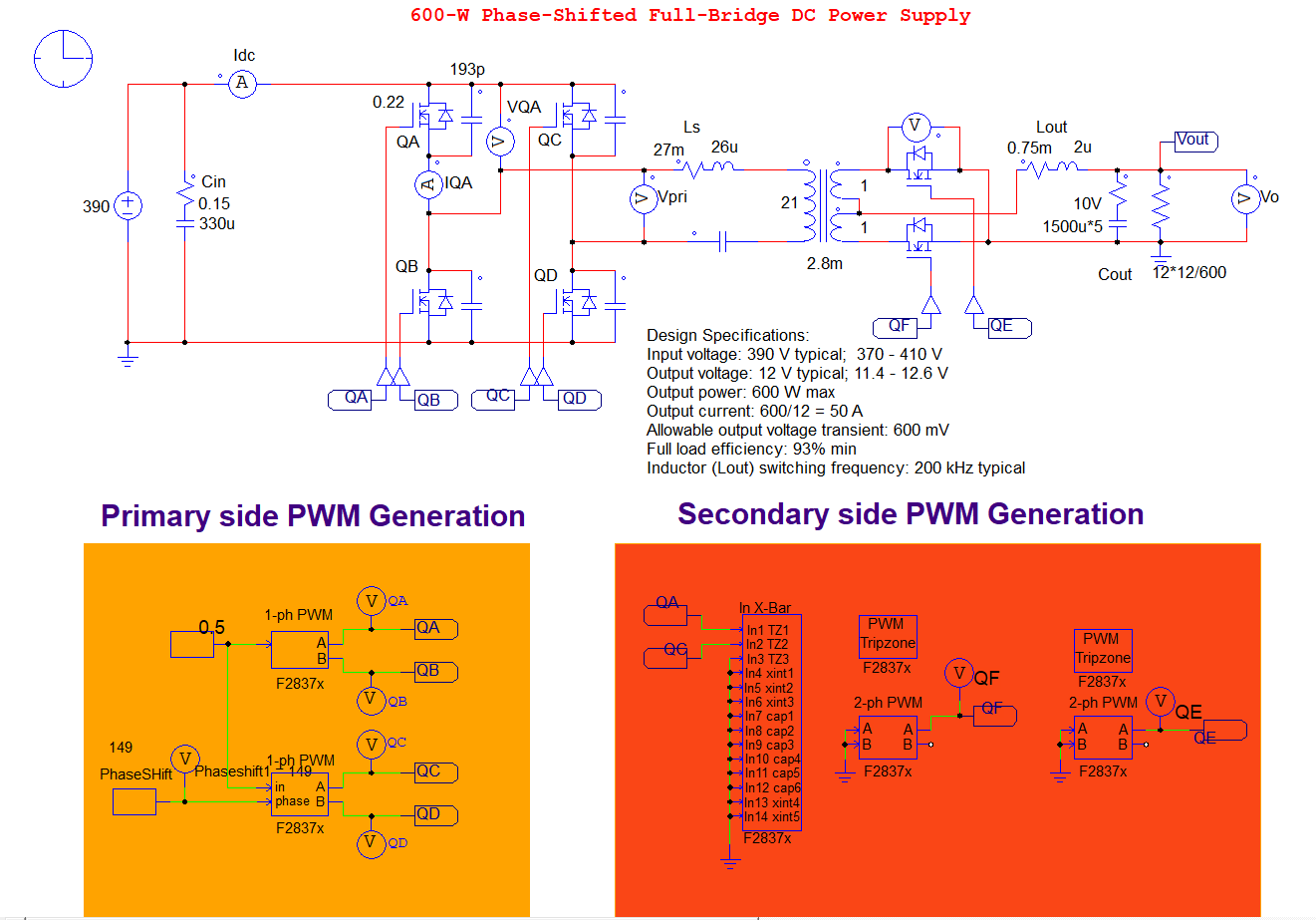
Fig 2: PSIM Implementation
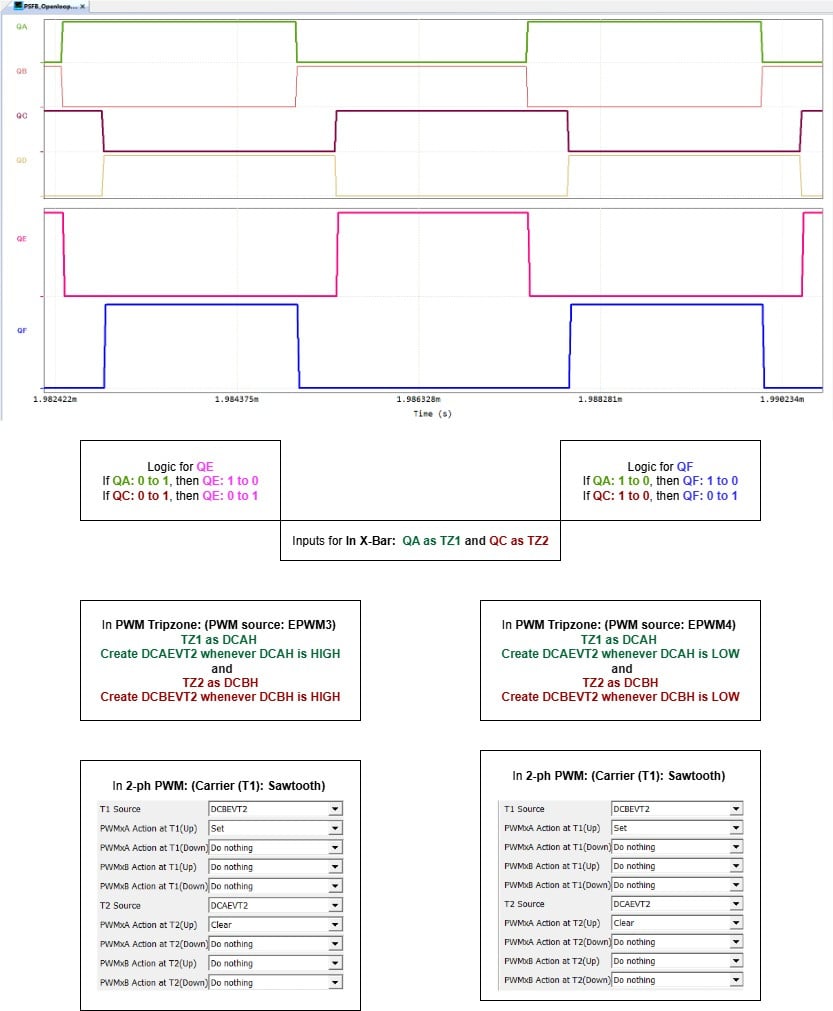
Fig 3: PWM Generation
Simulation Files:
Learn More:
- How do I know which PSIM elements are code gen compatible? - Altair Community
- Defining a State Machine for Embedded Code Generation - Altair Community