When launching PSIM, users can access a wide range of example simulations covering various Power Electronics applications. Among these, there are numerous examples focused on renewable energy systems, particularly Photovoltaic (PV) Arrays. In this article, we will explore a specific example involving a Buck Converter regulated by a Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm. Before diving into the example, let’s first understand what an MPPT algorithm is.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Algorithm
MPPT is a dynamic optimization technique used to continuously adjust the operating point of photovoltaic modules, ensuring they deliver maximum power output. This method is crucial for maximizing energy extraction and enhancing the overall efficiency of solar energy systems. By intelligently following the Maximum Power Point (MPP) on the Power-Voltage (P-V) curve, MPPT algorithms enable PV systems to operate at their optimal performance level.
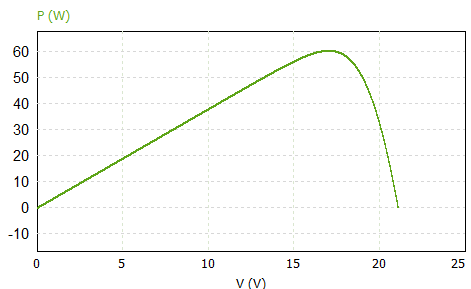
The peak of this curve can be determined using the following equations :
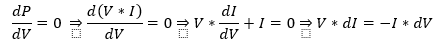
Buck Converter – MPPT – First differential Order
The example we’ll be working with is titled “Buck Converter – MPPT – First Differential Order.” It comes pre-installed with PSIM and can be accessed by navigating to: Files > Open Examples > Renewable Energy > Solar Power > Buck Converter – MPPT – First Differential Order.
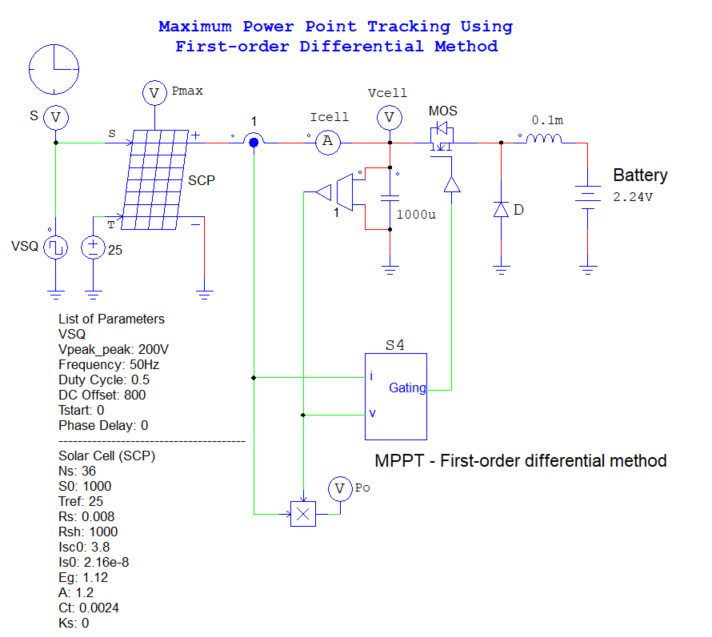
In this configuration, the photovoltaic (PV) array is linked to a constant voltage source via a buck converter. The converter is actively controlled to maximize power extraction from the PV array. To achieve this, the MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) block is properly configured to regulate the converter’s operation.
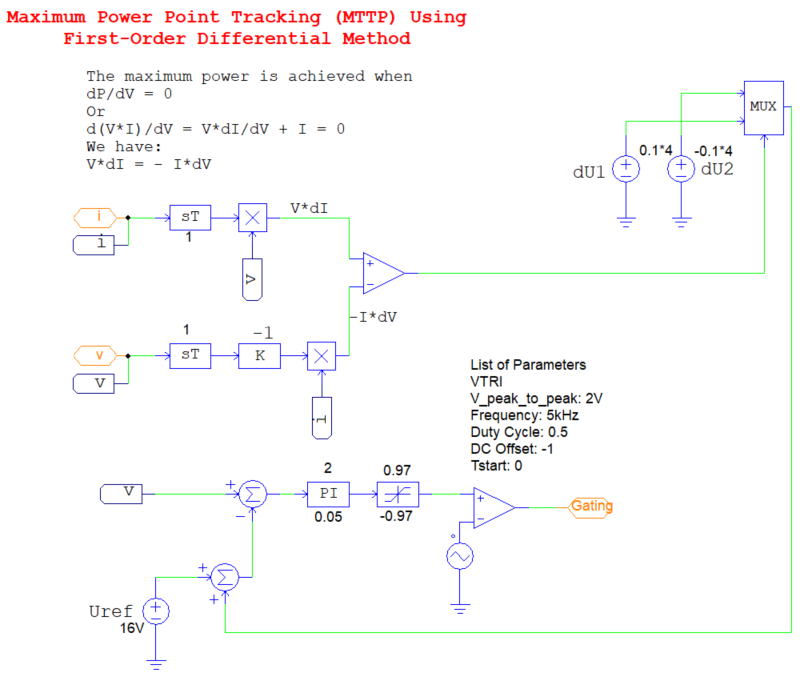
In this implementation, the system continuously compares both sides of the mathematical expression described earlier to determine the optimal operating point. Based on this comparison, it dynamically adjusts the duty cycle of the buck converter to ensure maximum power output from the PV array.
PSIM Solar module
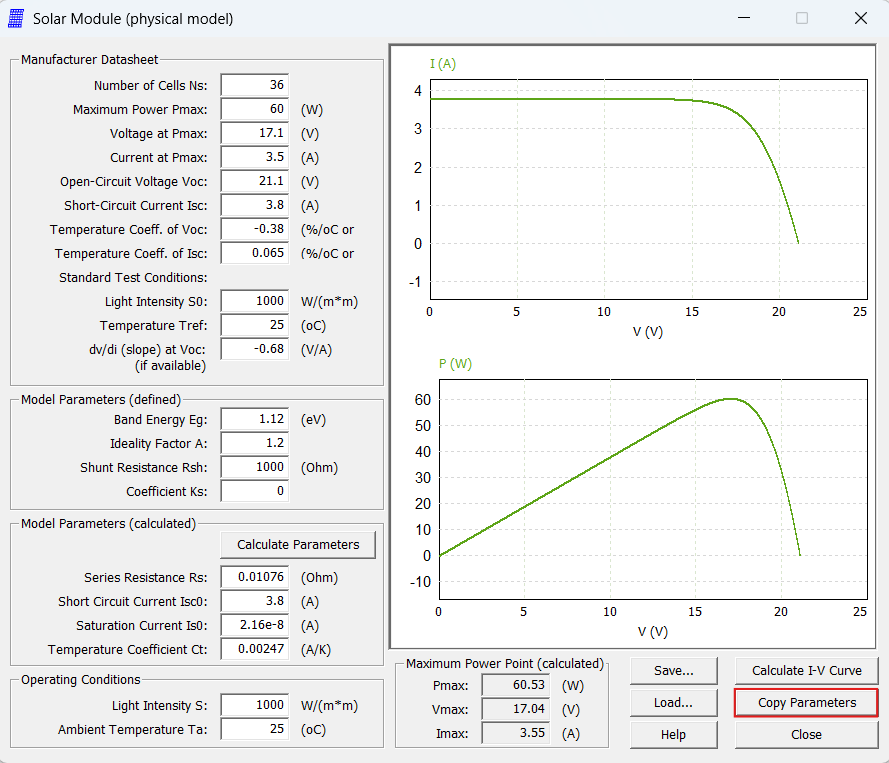
The Solar Module (Physical Model) utility, found under the Utilities tab in PSIM’s toolbar, is a powerful tool for defining the parameters of a specific solar module. It allows users to quickly model and analyze the electrical characteristics of a PV module. By generating the I-V and P-V curves, users can gain valuable insights into the module’s behavior under various environmental conditions.
One particularly useful feature is “Copy Parameters,” which enables seamless transfer of the configured module parameters directly into an existing PV array within your simulation.
Simulation Examples to Explore
Feel free to explore more simulation examples related to Power Electronics including:
- Multiple kinds of converters (Multi-level, Resonant etc)
- Energy Storage (Batteries, Supercapacitors)
- Renewable Energy ( Wind Power, Solar power)
- Electromagnetic Interference
- and even more