- RESEARCHER
- Pelayo Valle Pello
- INSTITUTE
- University of Oviedo, Spain
- DEPARTMENT
- Construction and Manufacturing Engineering
- SUPERVISOR
- Juan Jose del Coz Diaz
- TIMELINE
- Completed (10/2015 - 06/2016)
The aim of the project was to carry out a numerical model of the behavior of cement-based materials. It was based on a discrete element model with a particle interaction defined by the bonded-particle model (BPM). This numerical model was held in order to accurately reproduce the wear resistance of these materials. The numerical analysis approach to abrasive wear of cement-based materials was based on experimental tests. To simulate the wear test, a discrete element model was implemented using EDEM software. The wear of the specimen was measured in EDEM as the loss of particles from the specimen in contact with the disc. Design of experiments technique (DOE) and the response surface methodology (RSM) were used to study and determine the influence of parallel bond parameters such as critical normal stress and critical shear stress. It was found that the simulations performed in EDEM accurately reproduce the qualitative behavior of cement-based materials under abrasive wear. Furthermore, it was found that this methodology can offer reliable approximation models to predict the field-scale behavior of cement-based materials when abrasive forces are applied between surfaces and moving objects during service.
RESULTS
Publication under review entitled "˜Numerical analysis approach to abrasive wear of concrete: experimental and numerical methods.'
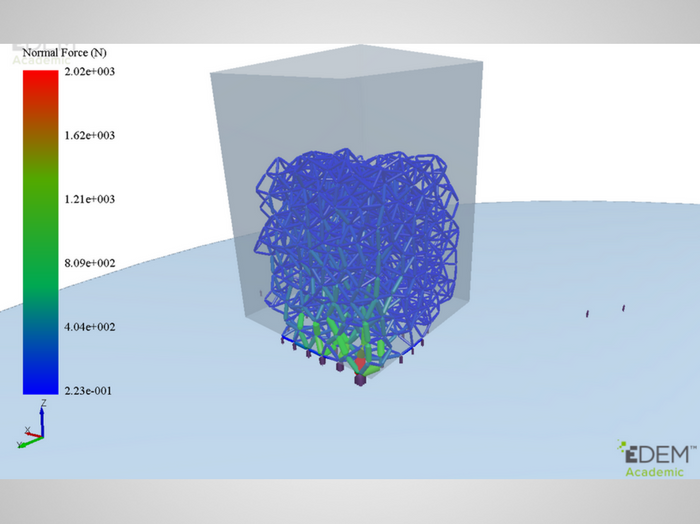 Fig. 1. Coloring bonds of cement-based particles
Fig. 1. Coloring bonds of cement-based particles 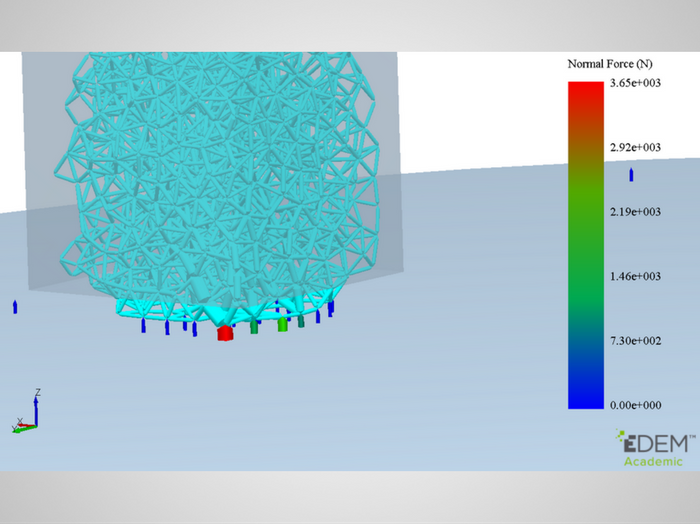 Fig. 2. Coloring contacts between cement-based particles
Fig. 2. Coloring contacts between cement-based particles
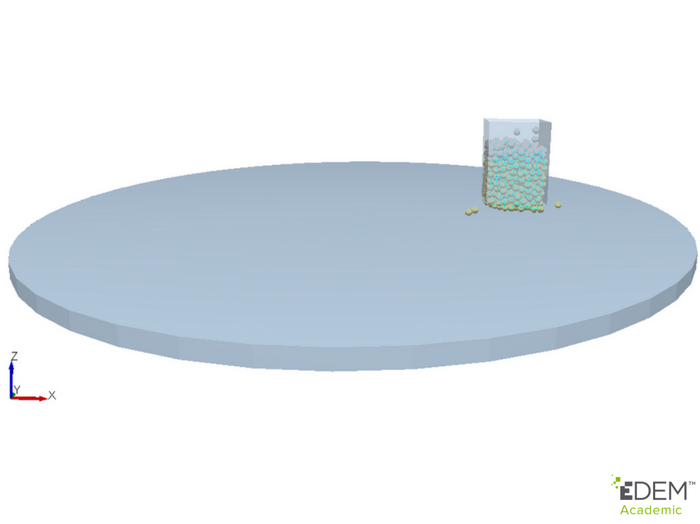
Fig. 3. Illustration of geometry wear
EDEM software accurately simulates the behavior of cement-based materials using model interaction based on Hertz-Mindlin with bonding. EDEM Analyst provides information about bond status throughout the simulation. EDEM is a very useful tool for simulating wear test conditions, including the physics and the geometry.