The need for fibers in EDEM
Fibers are fundamental in some industries like Agriculture, Construction, Fabrics Manufacturing or Battery Manufacturing, among others. EDEM has been used in the past in simulations within these fields, but it did not offer a model specifically designed for fibers. The Fibers Bonding model is a contact model designed and coded to bond particles which exhibit a main direction (the axis of the fiber), like sphero-cylinders. It was first published with EDEM 2025.
From its conception, the Fibers Bonding model aimed at modeling fibers with the following characteristics:
- Initially curved, stress-free shape
- Bonding at any position of the particle
- Presence of bifurcations
- Bonding of heterogeneous particles (length, thickness, density, …)
- Accurate solution of the mechanics of the fiber, based on beam theory
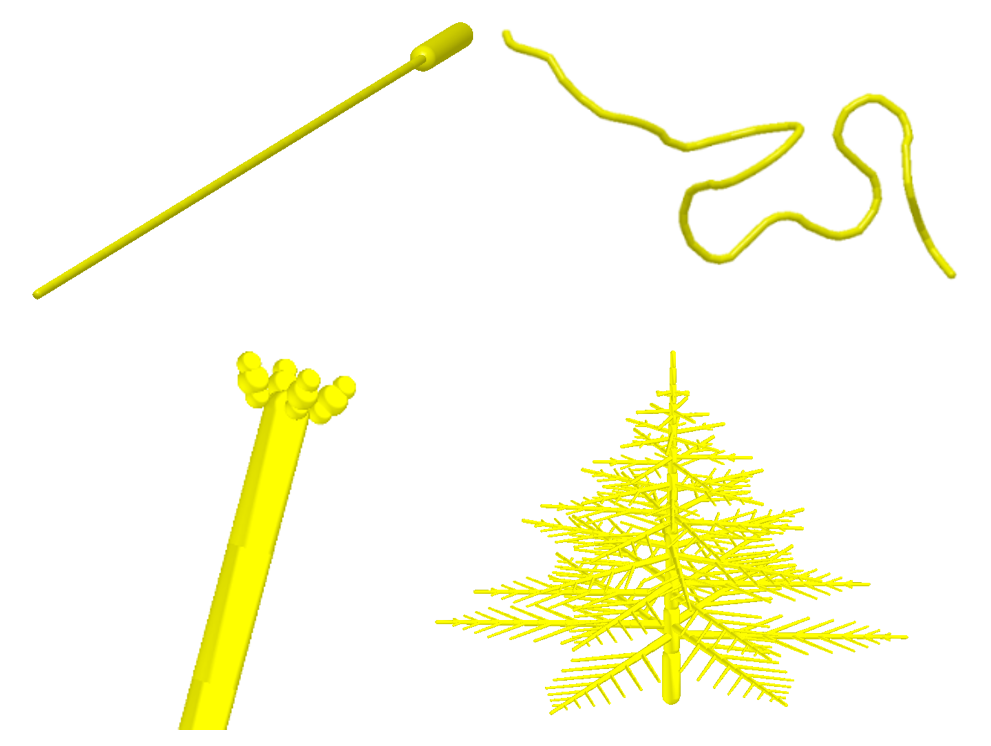
Figure 1. Examples of initial, stress-free shapes of fibers
By following an innovative EDEM formulation, very realistic simulations of fibers are possible:
Video 1. Hay stirring
Video 2. Toothbrush
Video 3. Barbed wire rolling
Video 4. Basketball and net shake
Elastic formulation
The force between two bonded particles follows the following expression:
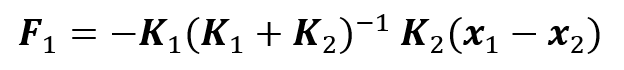
Where
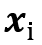 are the positions of the bonding point on both particles, and
are the positions of the bonding point on both particles, and
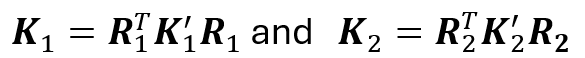
are the force stiffness matrices (3x3) and
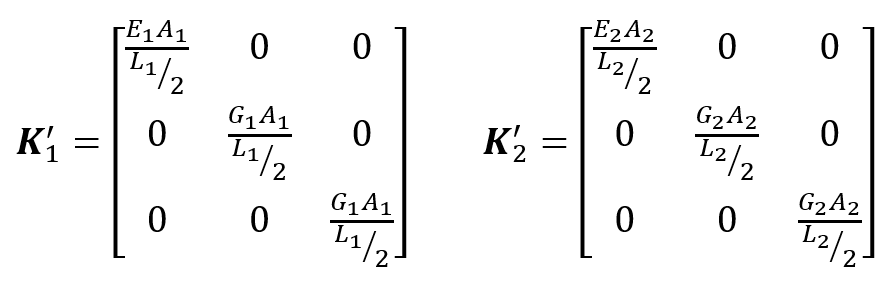
are the expressions of the stiffness matrices oriented with the particles, to establish accurately what are axial or shear contributions.
The equations for the torques are relatively similar but they involve extra complications which can be checked in the official documentation (help).
A variety of failure modes
In reality, fibers can mechanically fail by a wide range of mechanisms. The Fibers Bonding model provides two options to model the failure in EDEM 2025:
- Breakage
Video 5. Breakage of uncooked spaghetti in multiple locations
- Plastic bending
Video 6. Plastic bonds in a complex fiber
However, EDEM 2026 will extend the family of failure modes by adding many other types of breakage and plasticity, and also different types of buckling for fibers with hollow section. Watch the results of the 2026 prototype:
Video 7. Grass mower modeled with the failure modes available in EDEM 2026
Longer particles, faster simulations
The typical discretization of fibers before the Fibers Bonding model used to be a collection of spheres, with the radius of the fiber. By using bonded sphero-cylinders, the number of particles can be reduced drastically (in some cases) and even more the number of contacts. Also, if desired, the sphero-cylinders can be overlapped for a smoother surface.

Figure 2. Reduction in the number of particles (and contacts, internal or with other fibers and walls)
A better damping method
The Fibers Bonding model features a damping method which barely penalizes the critical time step. Traditionally, viscous damping algorithms, based on relative velocities of adjacent particles, have required smaller time steps than the undamped solution, but the Fibers Bonding model features an innovative stabilization parameter to keep the same time step stable.