In this article, we demonstrate the implementation of bidirectional position control for a BLDC motor under variable load conditions. A custom simulation model has been developed, where both the desired position and external torque load can be provided from 3D mechanical systems.
Since PSIM is inherently a 1D system-level simulation tool, it cannot directly integrate 3D mechanical models. To overcome this limitation, we use Altair TwinActivate a systems modeling environment that enables the co-simulation of 1D and 3D systems.
Through co-simulation with tools like MotionSolve or EDEM within TwinActivate, external torque or load dynamics originating from 3D models can be accurately applied to the BLDC motor. This allows for realistic testing of motor control strategies under various physical conditions.
BLDC design and control implementation of PSIM is as shown in Figure 1.
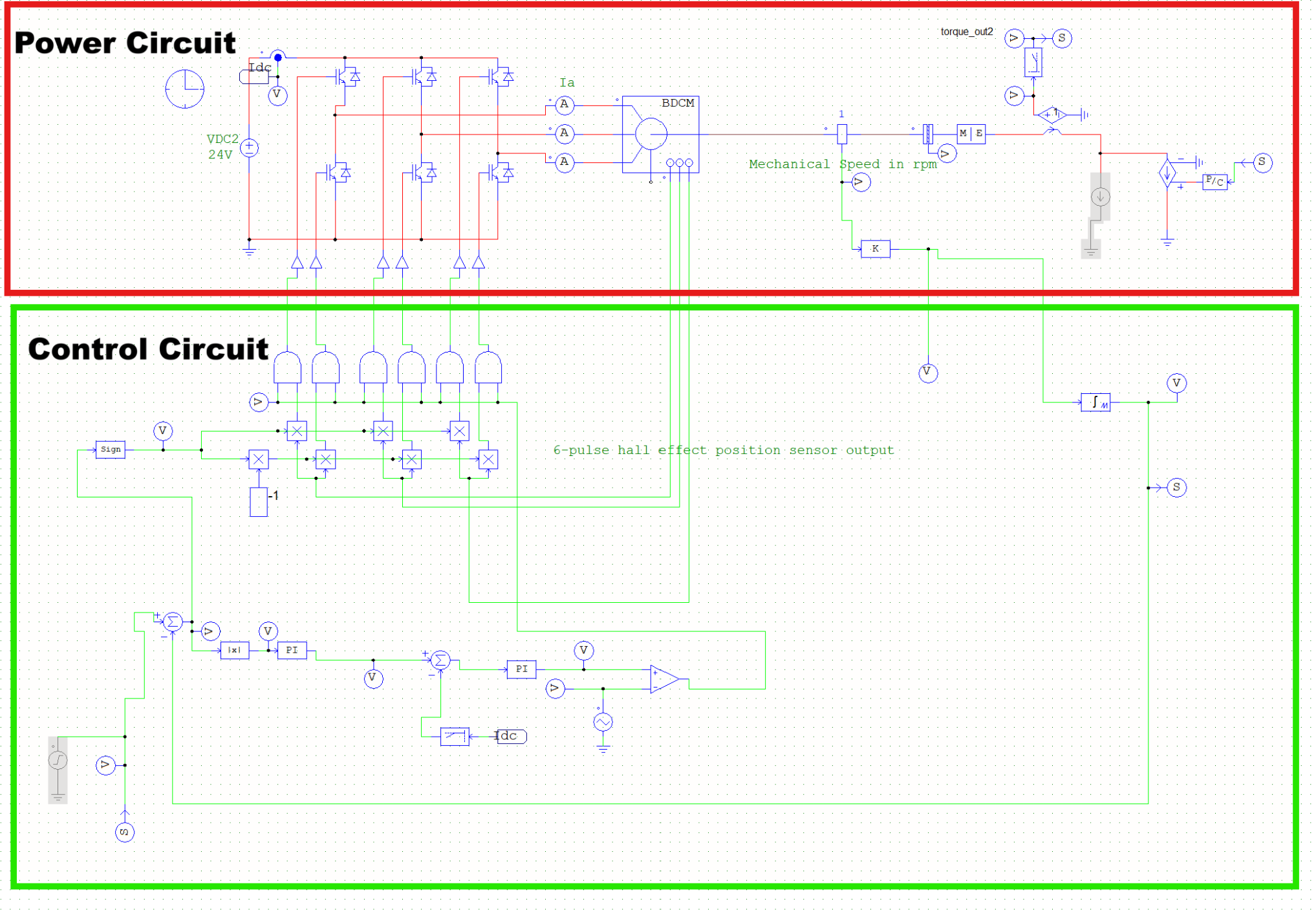
Figure 1
Here in this work, input data such as torque or position is applied to the system using external CSV files. This allows simulation of realistic, time-varying, and bidirectional loads using both positive and negative torque values. Both inputs are fed into Twin Activate (as shown in Figure 2).
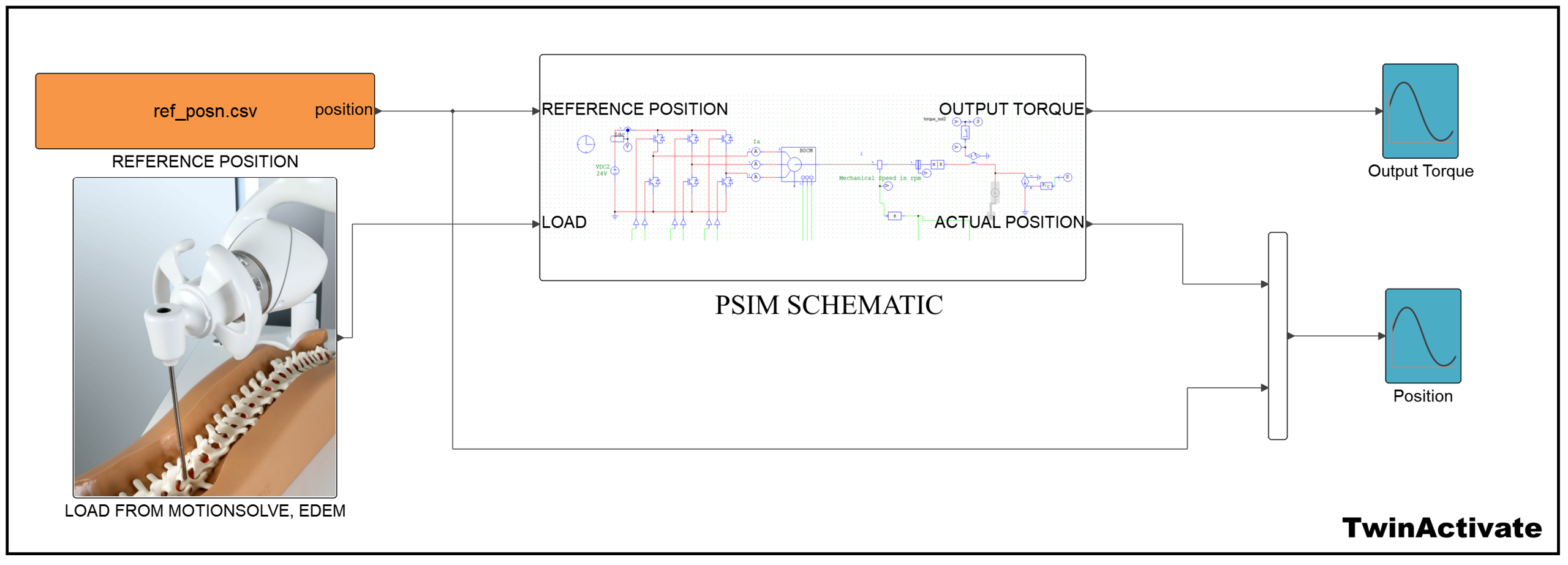
Figure 2
Simulation Results:
CASE 1.1: Constant Torque with sinusoidal input
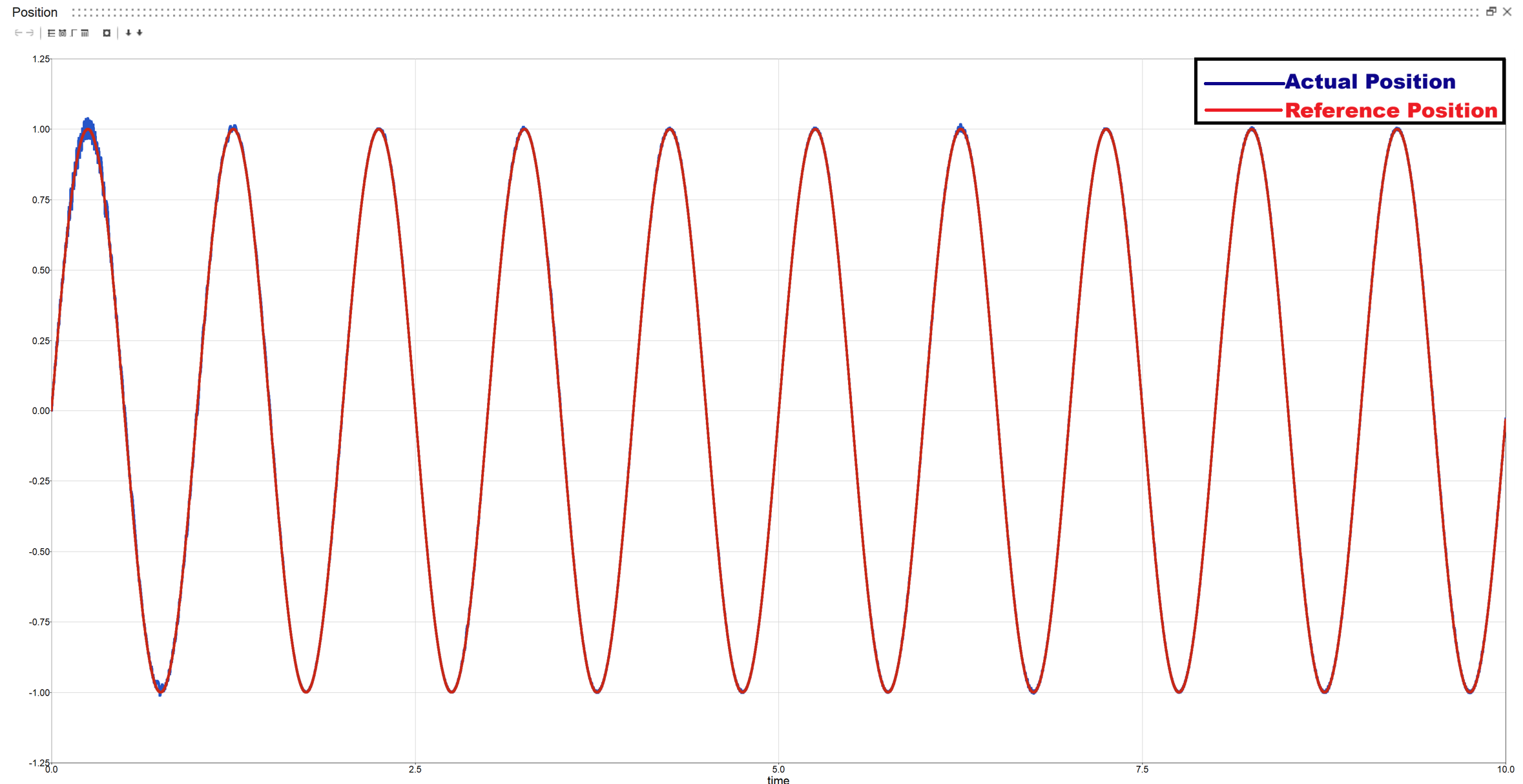
Actual vs Reference position
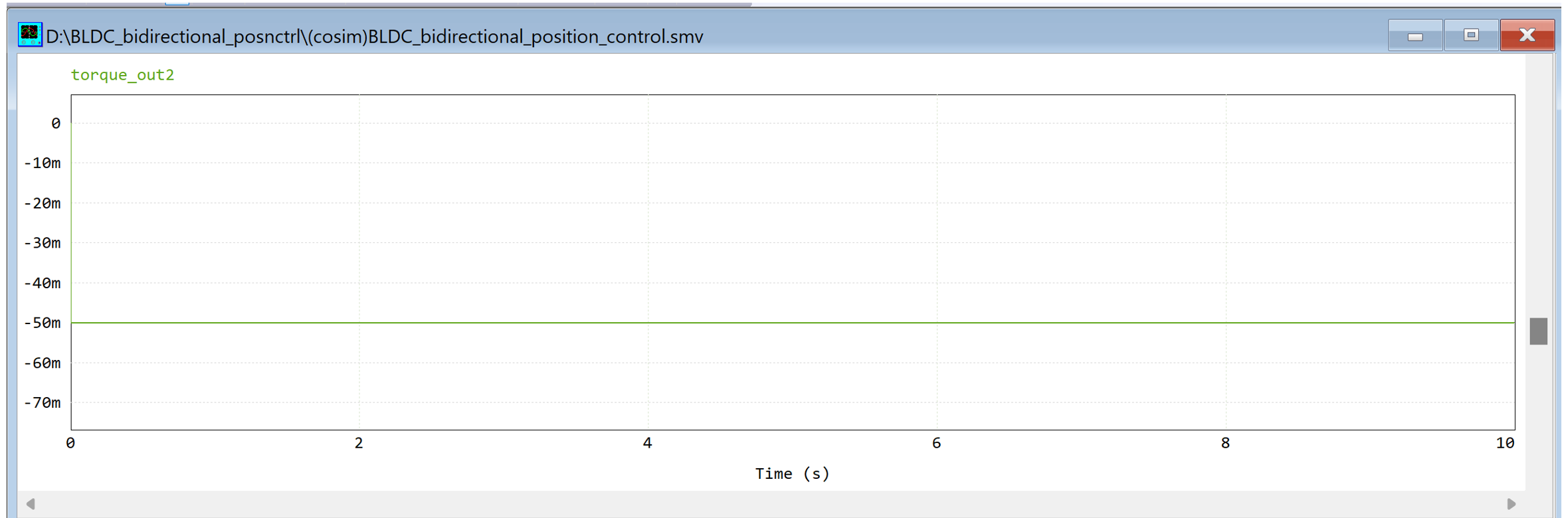
Electromagnetic torque (Generated from BLDC Motor)
1.2: Constant Torque with random input
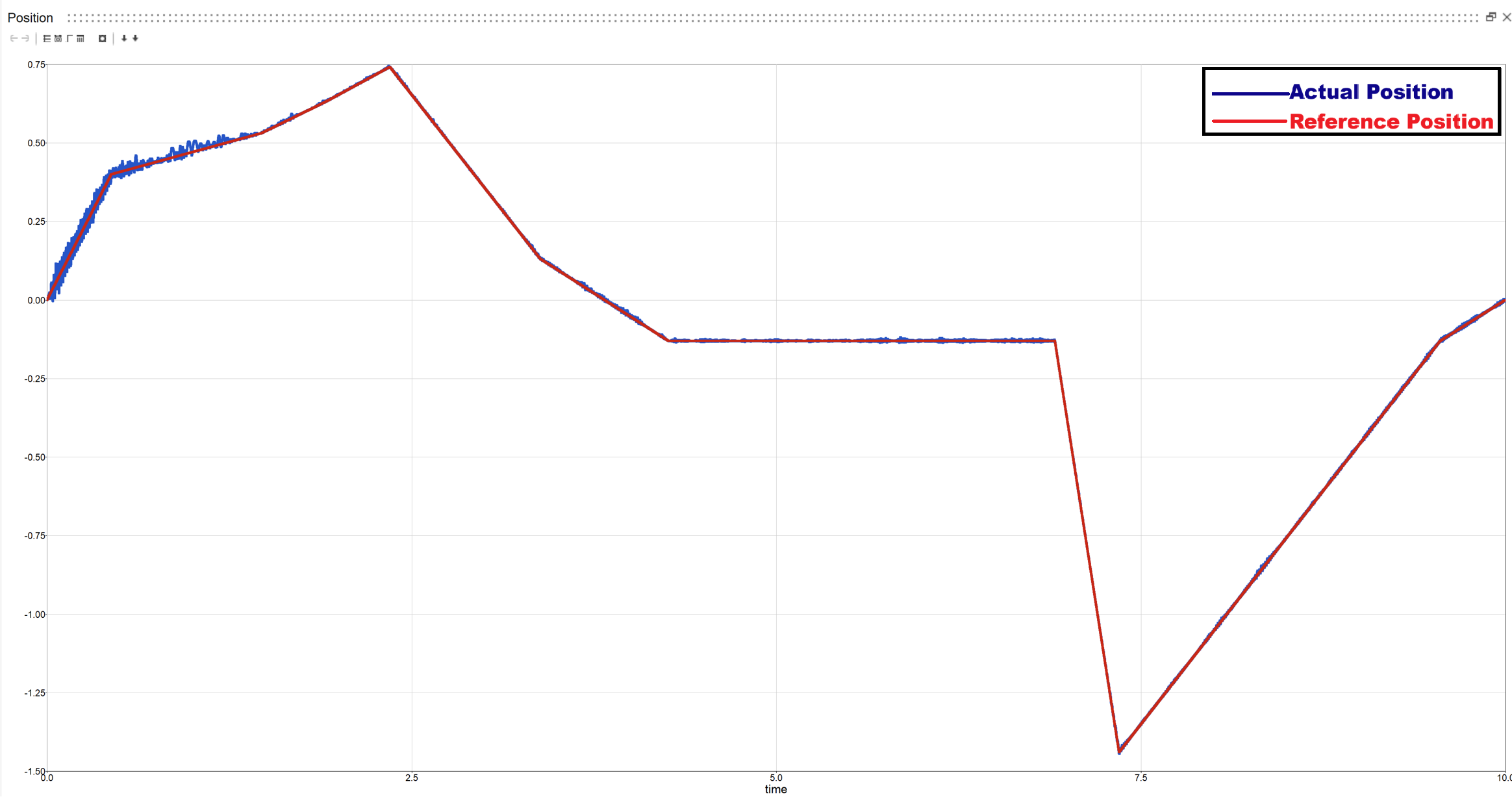
Actual vs Reference position
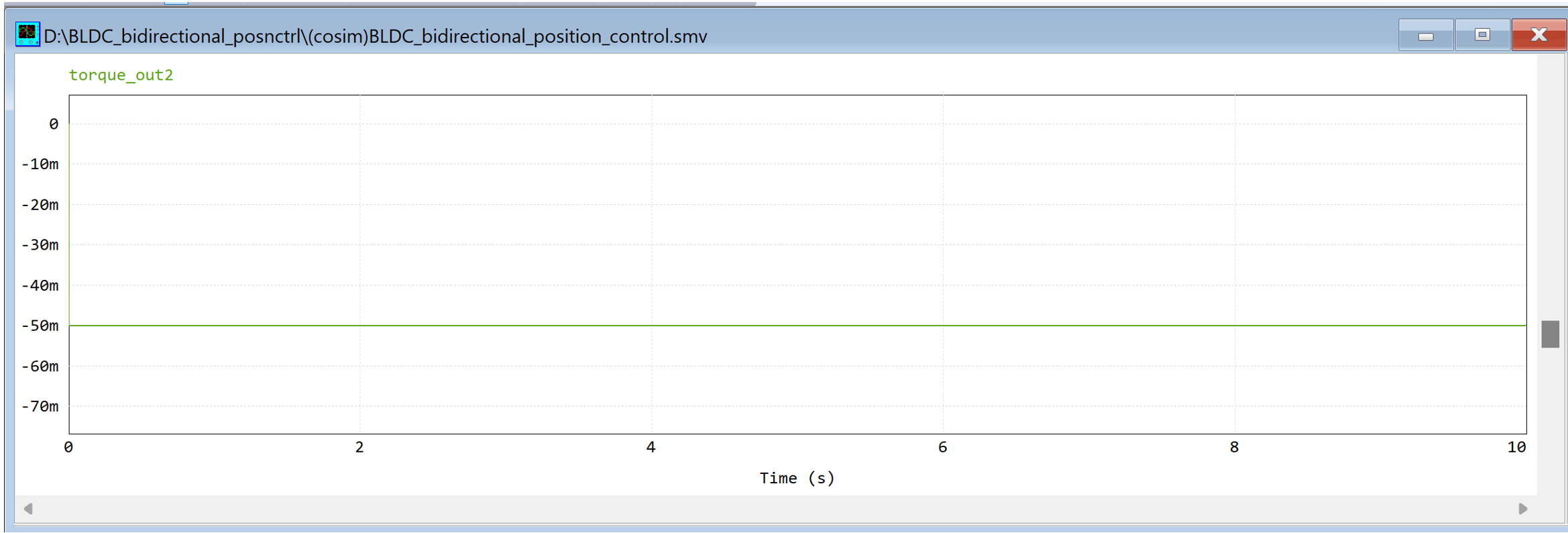
Electromagnetic torque (Generated from BLDC Motor)
CASE 2.1: Variable Torque with sinusoidal input
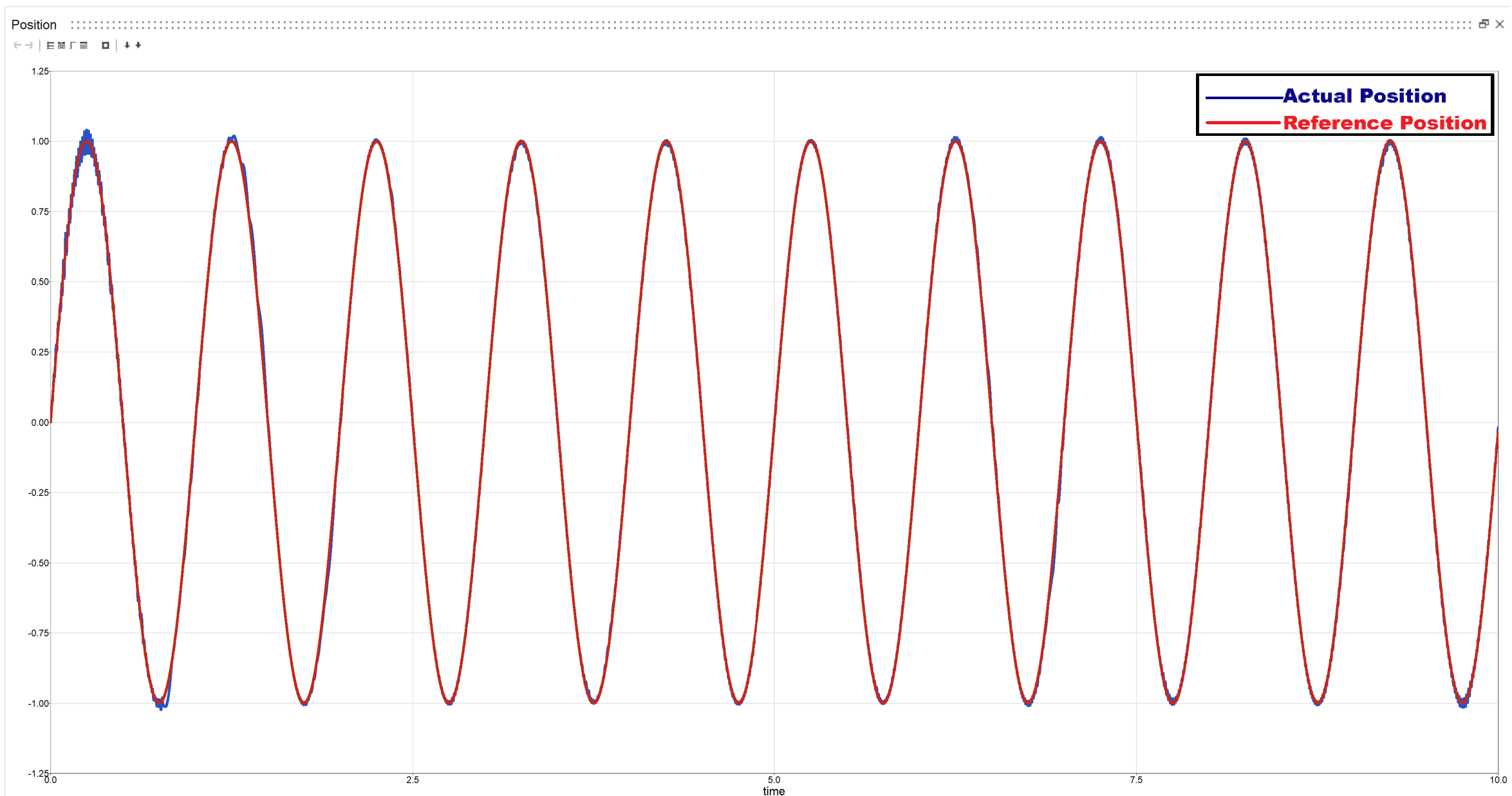
Actual vs Reference position
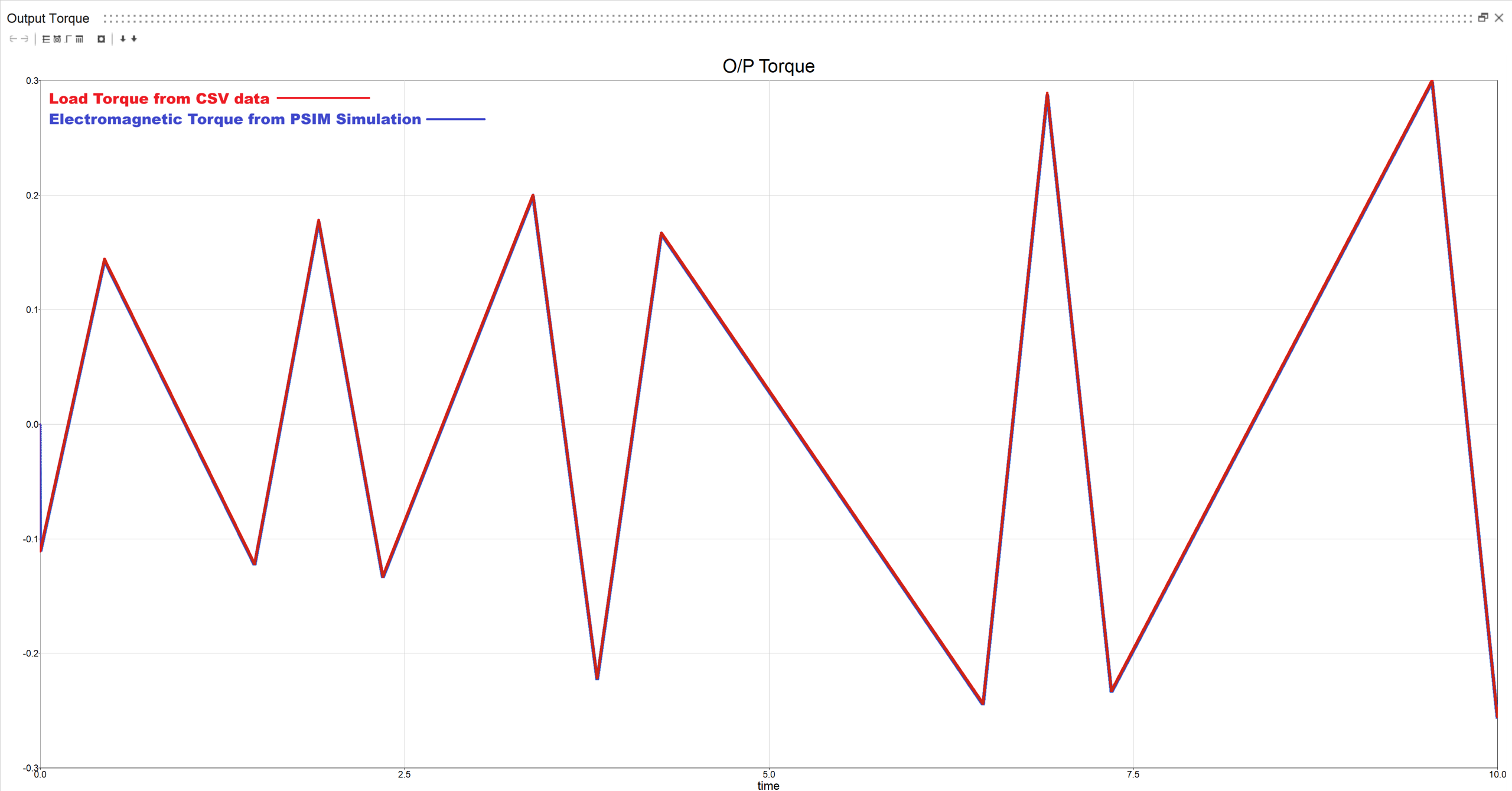
Electromagnetic torque from motor vs load torque
2.2: Variable Torque with random input
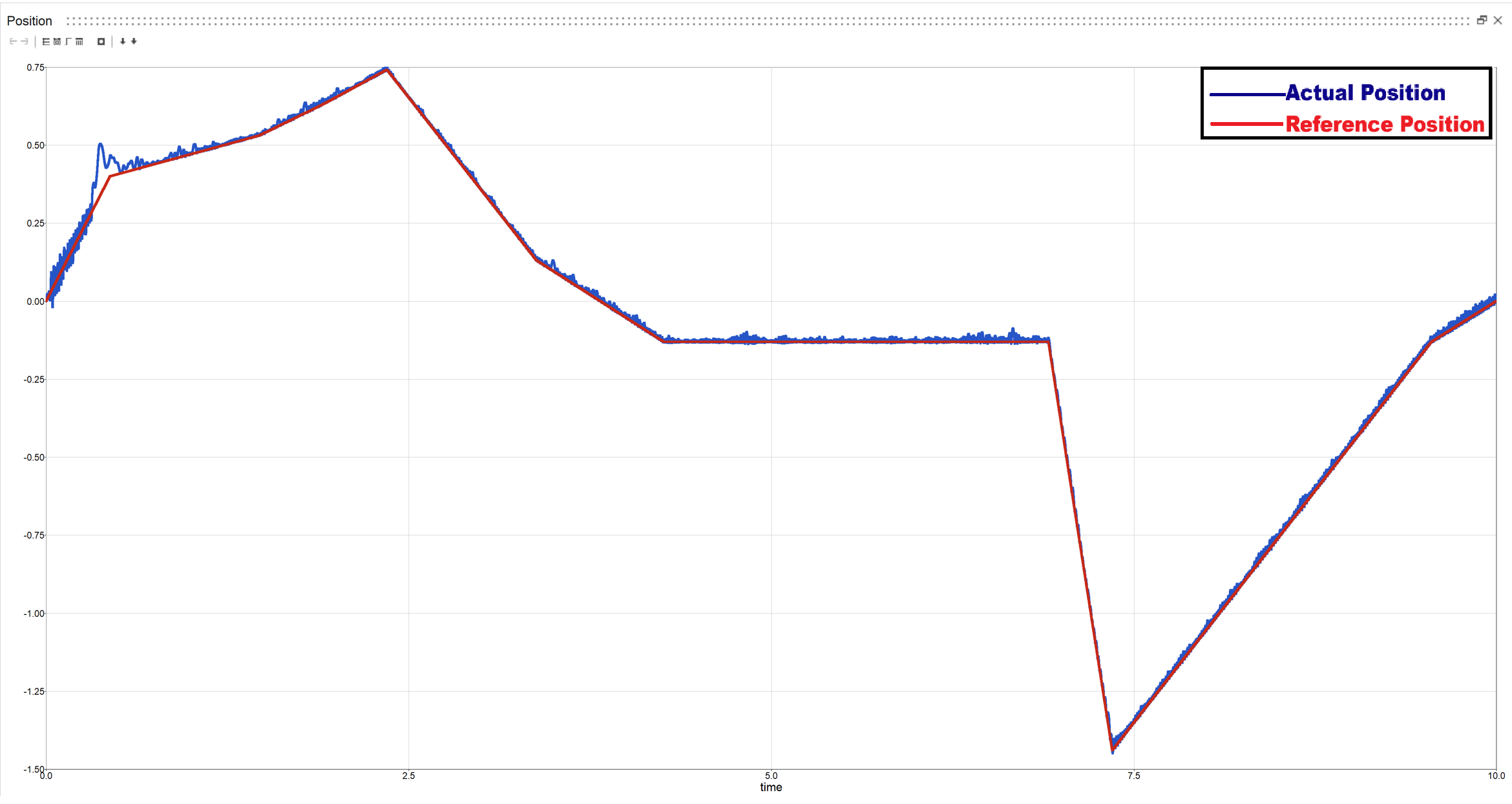
Actual vs Reference position
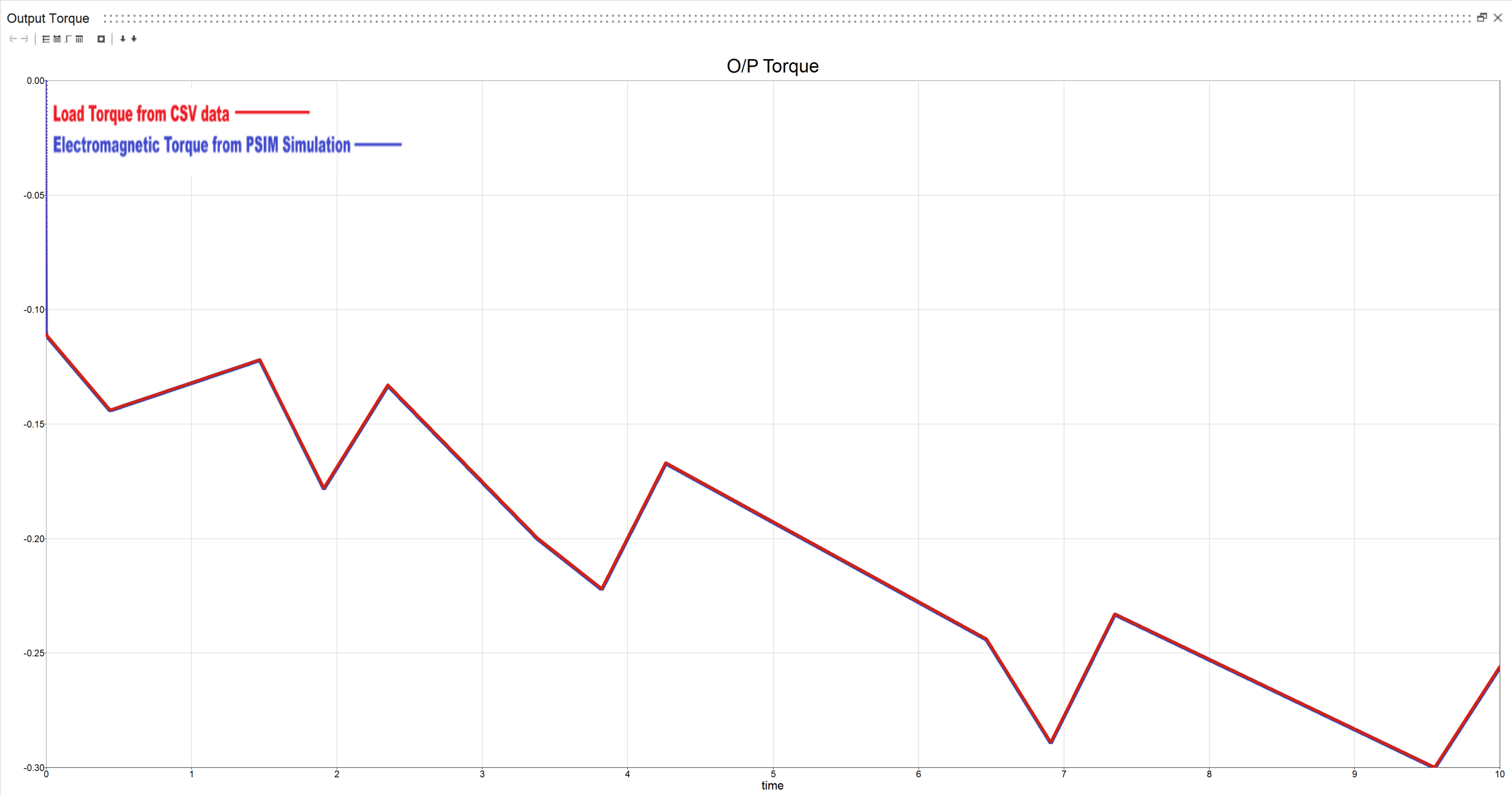
Electromagnetic torque from motor vs load torque
Files: