Aperture FreeSpace reflection
Hello all,
I want to implement a rectangular waveguide with a metal flange at the aperture. Intention is to see the reflection characteristic at the aperture-freespace boundary and the near field as a result of that. I wanted to know how exactly should I put my waveguide excitation so that I can only observe the aperture-freespace reflection coefficient. I also want to know how to put an infinite ground plane surrounding the aperture. For now, I am using a 5\lambda \times 5\lambda metal 2D surface. I am attaching my model to this thread.
Thanks in advance.
Answers
-
The waveguide source reflection coefficient will be the ratio of the incident vs reflected power. So any non-ideal flange (impedance match with free space) would deteriorate this coefficient.
If the flange causes higher order modes to be excited, at e.g the junction, you would need to set a higher number of modes to include (capture) at the waveguide port on the advanced tab of the waveguide port dialog. This will however require a finer local mesh setting on the waveguide port face.An aperture is allowed in an infite ground plane (Sommerfeld option, see Example guide A.10.2, 'aperture triangles in an infinite ground plane') but you won't be able to use a waveguide source with the infinite ground plane. This is not supported.
You would have to continue using the finite ground plane.0 -
Altair Forum User said:
The waveguide source reflection coefficient will be the ratio of the incident vs reflected power. So any non-ideal flange (impedance match with free space) would deteriorate this coefficient.
If the flange causes higher order modes to be excited, at e.g the junction, you would need to set a higher number of modes to include (capture) at the waveguide port on the advanced tab of the waveguide port dialog. This will however require a finer local mesh setting on the waveguide port face.An aperture is allowed in an infite ground plane (Sommerfeld option, see Example guide A.10.2, 'aperture triangles in an infinite ground plane') but you won't be able to use a waveguide source with the infinite ground plane. This is not supported.
You would have to continue using the finite ground plane.Is there any way I can avoid the reflection from edges of the ground plane? Like adding a resistive load on the finite ground plane at a distance so that no energy is reflected back? If it is possible, how can I do it?
0 -
Try a lossy coated surface around the outer parts of the ground plane.
An absorber has er=ur and and electric losses=magnetic losses.
How wide this surface should be, how thick, and what parameters to use is up to you.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
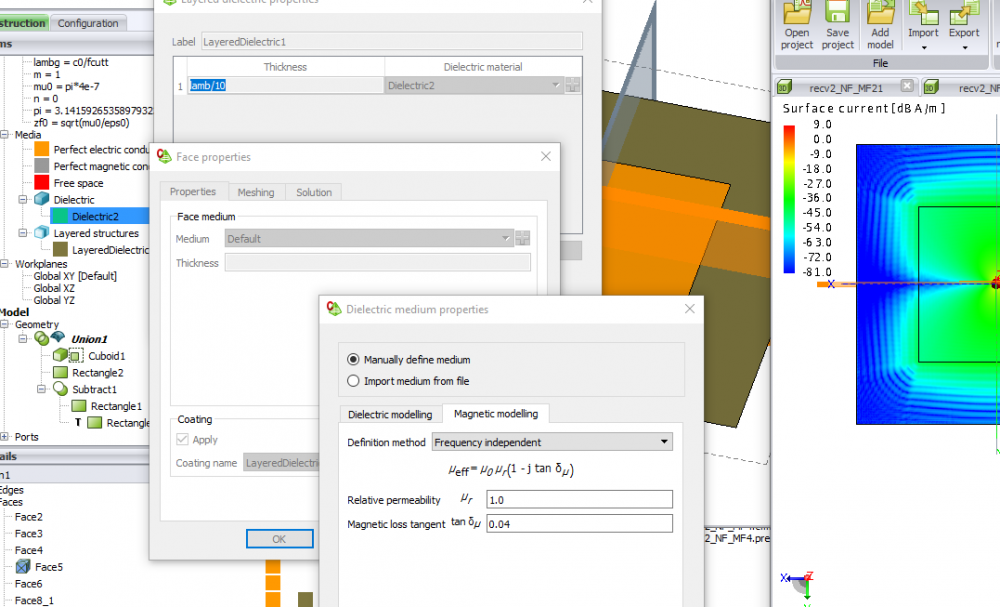
I assume you used a mesh of lam/25 because of the waveguide port. You can use a Coarse mesh setting and just set a local finer mesh on the waveguide port face in the details tree. This will save substantial resources.
0